Electrochemical analytical tools are widely applied to arsenic(III) detection and abundant achievements have been made. However, how to accurately detect and trace As(III) in groundwater has puzzled scientists for years and they have known that it depends on sensitivity of detection. Aiming at this, a study team managed to improve electrochemical sensing arsenic(III) using amino-functionalized graphene oxide decorated gold microelectrode, which was published in Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical.
Actually, detection of As(III) without interference in the real sample is a challenging task. Hence, analytical challenge for As(III) determination is to seek an reliable platform to realize the sensitive detection of ppb or sub-ppb levels of As(III) without interference from common coexisting substances under the mild condition.
In this work, with the synergy between the strong absorption capability of NH2-GO and the excellent electrocatalytic ability of Au microwire, the NH2-GO modified Au microelectrode shows the enhanced electrochemical performance toward As(III). “In the study, no obvious interference from other commonly coexisting ions on the determination of As(III) was observed, ” said Prof. HUANG Xingjiu, the team leader, a chemist at Institute of Intelligent Machines (IIM), Hefei Institutes of Physical Science
Meanwhile, in the lab, researchers preliminarily explored the possible mechanism of the enhanced stripping signal by using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) techniques. And they revealed the largest amount of adsorbed As(III) on the NH2-GO . High-resolution XPS and XANES results confirmed that the adsorbed As(III) onto the NH2-GO maintains the original As(III) oxidation state, which are beneficial to the sensitive and accurate analysis of As(III).
This work sheds new light on the development of novel sensing materials to analyze toxic ions based on the concept of adsorbent-assisted electrochemical analytical.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21377131, U1532123, 61474122, 21475133,21277146, and 61573334). The authors thank Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (beam line BL14W1) for providing measurement time. X.-J. Huang acknowledges the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) Interdisciplinary Innovation Team of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, China, for financial support.
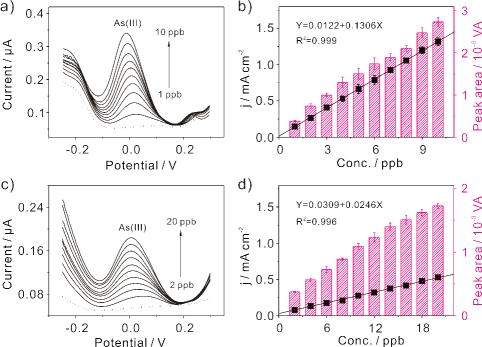
Figure 1. Electrochemical detection of As(III). SWASV responses of a) NH2-GO and c) GO modified Au microelectrode toward As(III), respectively. b) and d) The fitted linear equation of the stripping current and the concentration of As(III), respectively. (Imaged by YANG Meng)
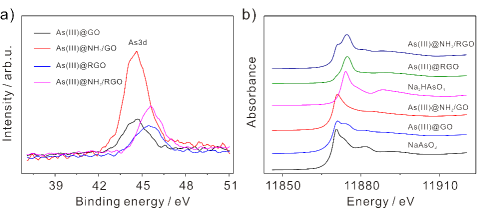
Figure 2. Electrochemical sensing mechanism studies. a) high-resolution XPS spectra of As3d signature region after As(III) adsorption on the GO, NH2-GO , RGO, and NH2-RGO , respectively. b) Normalized XANES of As K-edge in As-adsorbed. (Imaged by YANG Meng)
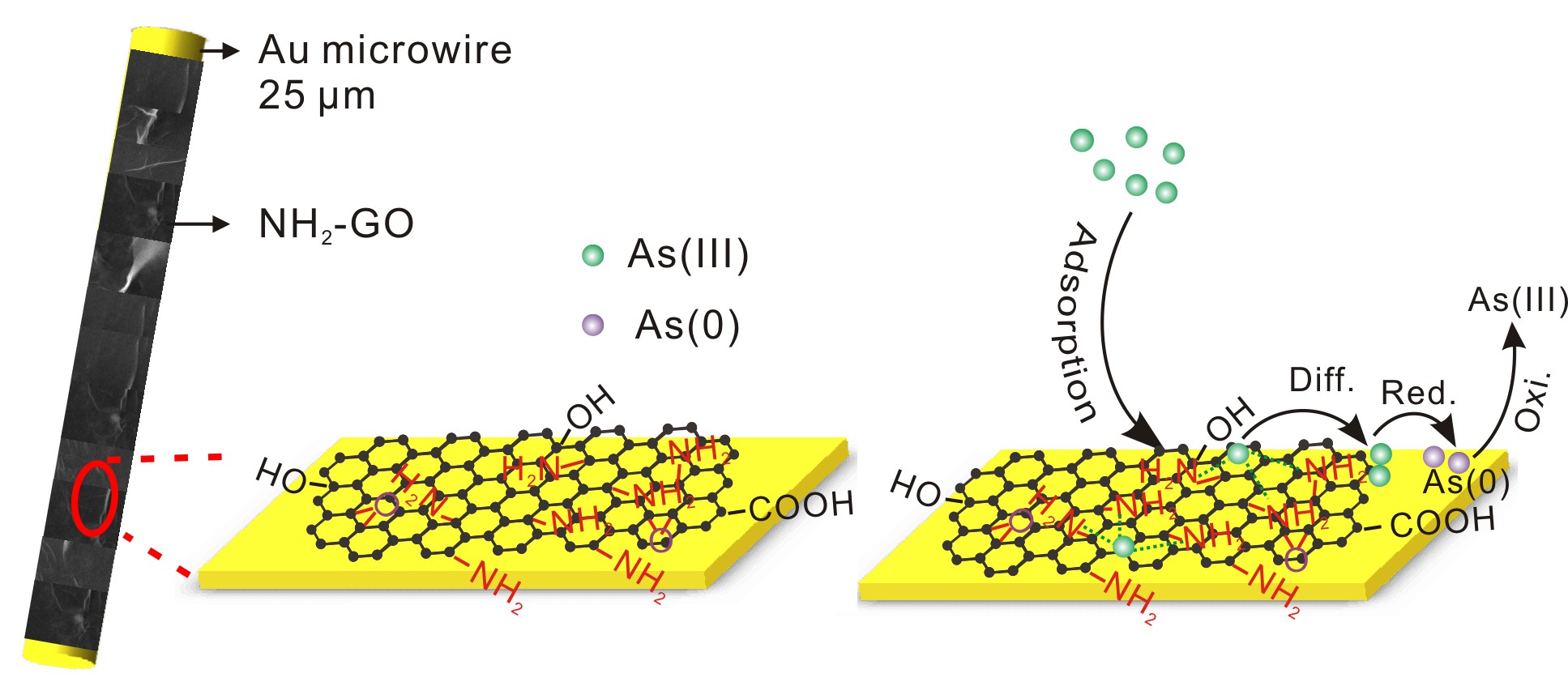
Schematic of in situ electrocatalysis for As(III) detection on NH2-GO modified Au microelectrode (Image by YANG Meng)
Contact:
HUANG Xing-Jiu
Institute of Intelligent Machines (http://english.iim.cas.cn/)
Hefei, Anhui 230000, China
Tel: 86-551-6559-1167
Email: xingjiuhuang@iim.ac.cn
 Tel: +86-551-65591206
Tel: +86-551-65591206
 Fax: +86-551-65591270
Fax: +86-551-65591270
 Emai: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
Emai: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
 350 Shushanhu Road
350 Shushanhu Road