Scientists with Institute of Solid State Physics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science developed nonprecious metal catalyst with better catalytic activity, selectivity and stability. The research was published in Advanced Materials.
Biomass represent the most abundant renewable resources on earth. With suitable catalysts, biomass could produce fuels and chemicals as replacement of the rapidly diminished fossil resource.
The heterogeneous catalytic selective hydrogenation has been one of the most widely used approaches in the fuels and chemicals producing. It is especially important to convert biomass-derived organic molecules into high value-added chemicals due to their rich oxygen contents.
Till now, the industrial hydrogenation catalysts are almost exclusively made of high cost metals. Cheap and earth-abundant materials based catalysts is therefore in urgent demand.
The researchers reported, for the first time, the use of nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes confined Co nanoparticles (NPs) with Co-Nx active sites derived from ZIF-67 as highly active and stable catalyst for selective hydrogenation of various biomass-derived organic compounds.
Such type of active sites could selectively hydrogenate aldehyde, ketone, carboxyl and nitro groups of biomass-derived compounds into value-added fine chemicals with performances equal to or better than the reported state-of-the-art precious and nonprecious metal based heterogeneous catalysts.
The reported approach could be adopted to create other forms of catalytic active sites from other nonprecious metals. More importantly, this research provides a new and effective way for the preparation of highly efficient nonprecious metal based hydrogenation catalytic materials, and provides a certain basis for the understanding of new hydrogenation active sites.
Link to the paper: Nitrogen‐Doped Carbon Nanotube Confined Co–Nx Sites for Selective Hydrogenation of Biomass‐Derived Compounds
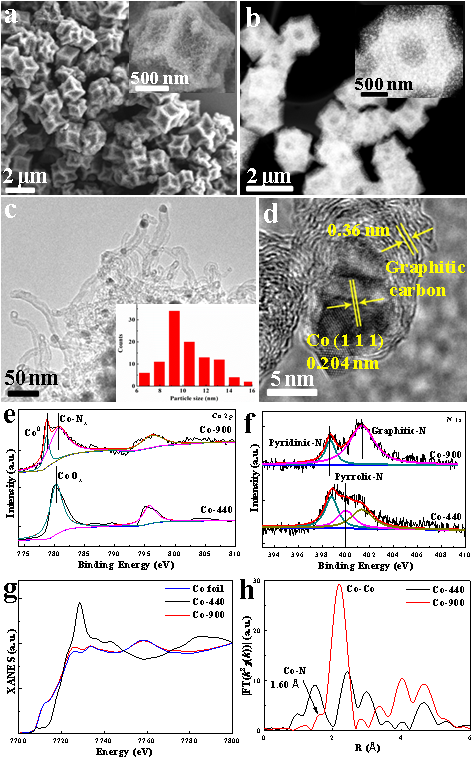
Figure 1. (a-d) Typical SEM images (Inset: high magnification image), HAADF-STEM images (Inset: high magnification image) and HRTEM images (Inset: Co NPs size distribution); (e-f) Co 2p and N 1s spectra; (g) Co K-edge XANES spectra; (h) Comparative k3-weighted x(k)-function of EXAFS spectra (Image by GONG Wanbing)
Contact:
ZHOU Shu
Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (http://english.hf.cas.cn/)
Email: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
 Tel: +86-551-65591206
Tel: +86-551-65591206
 Fax: +86-551-65591270
Fax: +86-551-65591270
 Emai: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
Emai: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
 350 Shushanhu Road
350 Shushanhu Road