A study team with Hefei Institutes of Physical Science revealed the importance of PKMYT1 in breast carcinogenesis, shedding new light on breast cancer treatment.
Breast cancer is the most commonly occurring gynecological cancers around the world, and the number of new cases diagnosed each year is increasing.
Many cancer cells depend on G2 checkpoint mechanism regulated by WEE family kinases to maintain genomic integrity. Previous studies have shown that WEE family kinases are related to the occurrence of breast cancer, but their clinical application is very limited.
The research team used a set of bioinformatics tools to comprehensively analyze the expression of WEE family kinases and found that PKMYT1 was the only member that was frequently overexpressed in different subtypes of breast cancer.
Abnormally high expression of PKMYT1 indicates a poor prognosis, especially for some subtypes, such as luminal A / B and triple negative (TNBC).
In addition, the up-regulation of PKMYT1 was related to HER2-positive (HER2 +), basal-like, TNBC status, and Scarff, Bloom, and Richardson (SBR) classifications.
Co-expression analysis showed that PKMYT1 and Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) had a strong positive correlation, suggesting that PKMYT1 and PLK1 cooperated to synchronize the rapid cell cycle and high-quality genome maintenance to synergistically regulate the proliferation of cancer cells.
Their study may suggest that PKMYT1 is an attractive target for breast cancer treatment, and specific inhibitors or other interventions could be developed for it in the future, providing a new direction for breast cancer targeted therapy research.
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Anhui Provincial Nature Science Foundation and Anhui Province Key Laboratory of Medical Physics and Technology.
Link to the paper: Systematic expression analysis of WEE family kinases reveals the importance of PKMYT1 in breast carcinogenesis
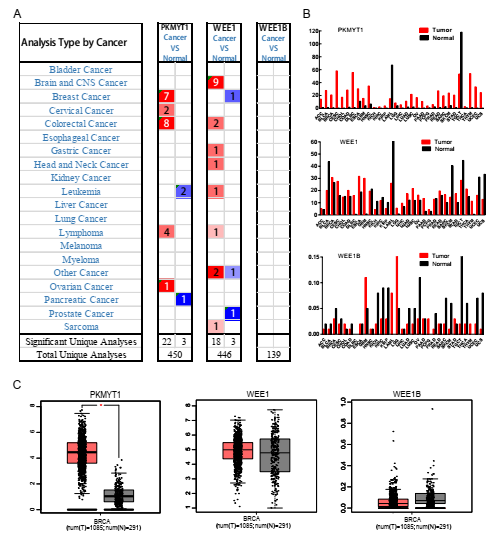
PKMYT1 mRNA expression was elevated in human breast cancer. (A) This graph generated by Oncomine indicates the numbers of datasets with statistically significant mRNA over-expression (red) or down-expression (blue) of PKMYT1, WEE1 and WEE1B (cancer tissues vs. corresponding normal tissues). The threshold was defined with the following parameters: p-value of 1E-4, fold change of 2, and gene ranking of 10%. (B, C) The GEPIA database verified that PKMYT1 gene expression was significantly upregulated in breast cancer tissues (BRCA) (n=1085) compared with normal breast tissues (n=291), *p<0.05. (Image by LIU Yu)
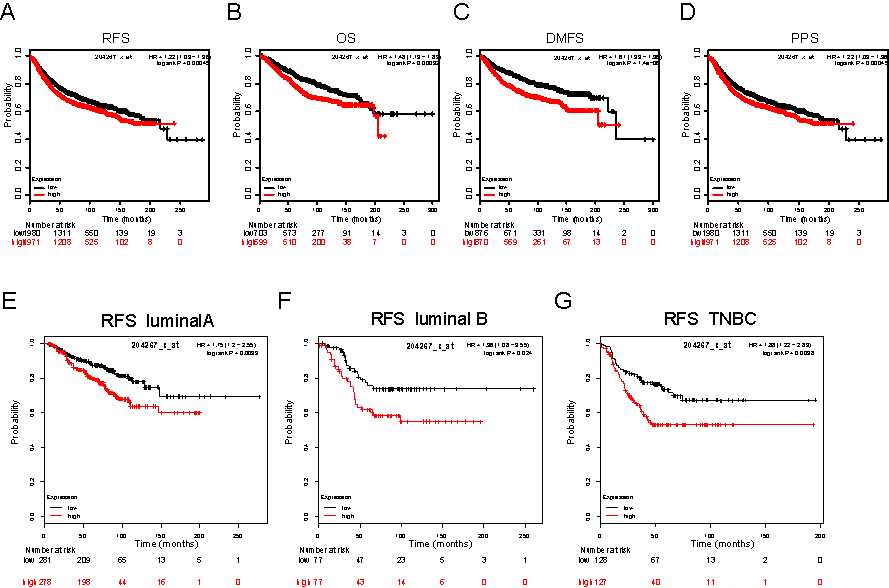
Prognostic significances of PKMYT1 gene expression in patients with breast cancer in the KM-plotter database. RFS, relapse free survival; OS, overall survival; DMFS, Distance Metastasis Free Survival; PPS, Post Progression Survival; HR, hazard ratio. (Image by LIU Yu)
Contact:
ZHOU Shu
Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (http://english.hf.cas.cn/)
Email: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
 Tel: +86-551-65591206
Tel: +86-551-65591206
 Fax: +86-551-65591270
Fax: +86-551-65591270
 Emai: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
Emai: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
 350 Shushanhu Road
350 Shushanhu Road