Scientists conducted a research which showed low-temperature plasma could help to remove 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl (PCB77), a typical polychlorinated biphenyl, from waste water.
The research, accomplished by Prof. HUANG Qing's group from the Institute of Intelligent Machines, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, proved that PCB77 could be degraded by low-temperature plasma effectively.
The group searched through different working gases such as helium, argon, oxygen, air and nitrogen for the plasma treatment of PCB77, and found that plasma discharge using inert gas, oxygen or air as working gas could have significant degradation effect.
For mechanism exploration, the researchers analyzed the contributions of hydroxyl radicals, H2O2, ozone, ultraviolet light and hydrated electrons in helium plasma, and found that hydroxyl radical plays the dominant role in PCB77 degradation.
Furthermore, it turned out that PCB77 could be dechlorinated to form biphenyl, and the benzene ring could be further broken to form acetophenone.
The toxicity evaluation suggested that the plasma treatment was a bio-safe method without causing secondary pollution.
This work therefore indicated a new effective way to treatment of POPs in the environment.
At present, many countries have environmental pollution problems caused by persistent organic pollutants (POPs) such as polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). They are often carelessly released into natural environment and thus constantly put human health at risk. However, due to lack of effective ways of degrading PCBs, researchers are still striving to explore new approaches to remove them from the environment.
Low-temperature plasma technology belongs to advanced oxidation processing (AOP) which has many advantages. In recent years, Prof. HUANG Qing's group are devoted in the treatment of polluted water with this technology, and have made some achievements in degradation of pollutants such as Cr6+, cyanobacteria, phycotoxin, polychlorophenols, dyes and antibiotics with various low-temperature plasma techniques, which further extends the application of low-temperature plasma technology in environment protection and pollution control field.
Link to this paper:Degradation of 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl (PCB77) by dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) non-thermal plasma: Degradation mechanism and toxicity evaluation
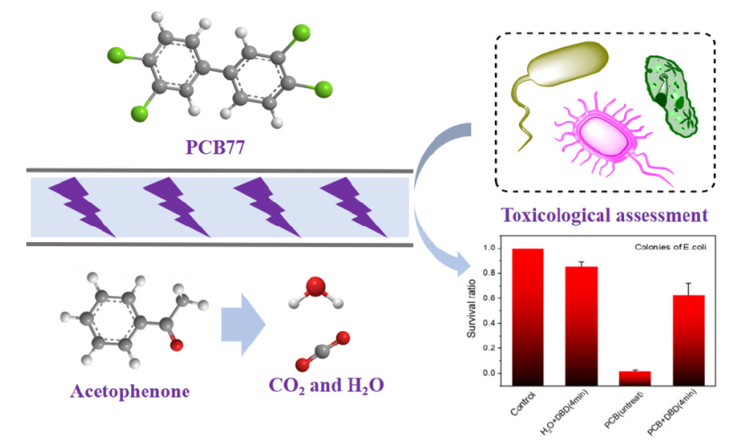
Schematic diagram of the experiment of using low temperature plasma to degrade PCB77(Image by FANG Cao)
Contact:
ZHOU Shu
Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (http://english.hf.cas.cn/)
Email: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
 Tel: +86-551-65591206
Tel: +86-551-65591206
 Fax: +86-551-65591270
Fax: +86-551-65591270
 Emai: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
Emai: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
 350 Shushanhu Road
350 Shushanhu Road