Recently, scientists at Institute of Solid State Physics (ISSP), Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) developed pseudocapacitive electrode for electrosorption of calcium ions, which is an effective way with high absorption capacity, selectivity and stability for water softening.
In this research, this team displayed how they achieved highly selective electrosorption of Ca2+ in a mixed solution of Na+, Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions when taking advantage of the intercalation effect of Ca2+ ions and utilizing CuHCF, for the first time, as a pseudo-capacitive electrode.
In the process, the highest electrosorption capacity of 42.8 mg.g-1 for Ca2+ ions was obtained at optimal applied voltage 1.4V. Especially, the raising trend of selectivity coefficient (Ca2+ over Na+) with increasing molar ratio of Na:Ca could be observed in the mixed solution of Na+ and Ca2+ ions, and the maximum selectivity coefficient of 3.05 was achieved on the Na+-to-Ca2+ ratio of 10:1. Researchers applied the first and second order kinetics and adsorption isotherm to analyze the pseudo-capacitive adsorption behavior of CuHCF electrode. By combining electrochemical characterization and molecular dynamics simulation technique, they clarified the intrinsic pseudocapacitive characteristics of CuHCF electrode for selective electrosorption of calcium ions.
Over 85% of accessible fresh water has been identified as hard water. Although water treatment technology for water softening-capacitive deionization (CDI) technique has aroused great concern, most of the electrode materials used in CDI are carbon-based materials, which lack high-efficiency selectivity of target ions.
This research work is of great significance for exploring CDI pseudocapacitive electrode materials with high efficiency and selective electrosorption of target ions and hard water softening by CDI technology.
Link to the paper: Selective Pseudocapacitive Deionization of Calcium Ions in Copper Hexacyanoferrate
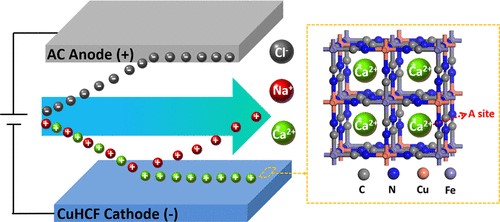
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of CuHCF-based capacitive deionization technology and selective electrosorption of calcium ions. (Image by XU Yingsheng)
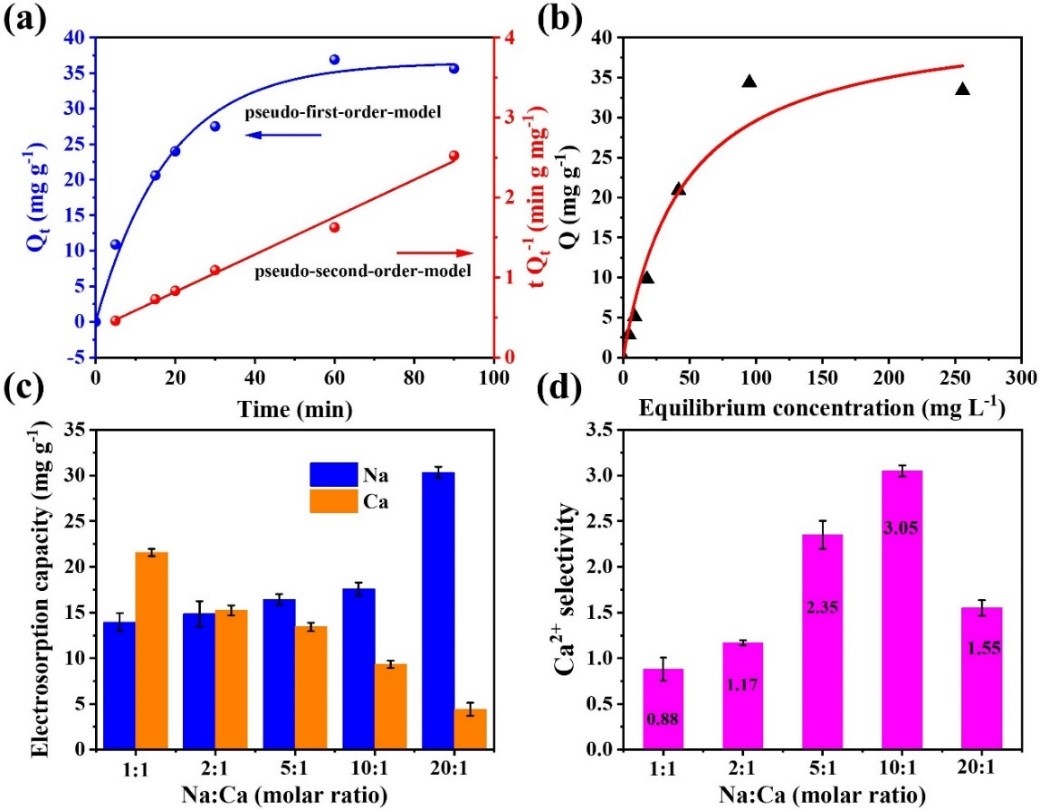
Figure 2. Pseudo-capacitive adsorption behavior of CuHCF electrode on selective electrosorption of Ca2+ ions. (Image by XU Yingsheng)

Figure 3. Electrochemical characterization and molecular dynamics simulation clarify the intrinsic pseudocapacitive characteristics of CuHCF electrode for selective electrosorption of calcium ions. (Image by XU Yingsheng)
Contact:
ZHAO Weiwei
Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (http://english.hf.cas.cn/)
Email: annyzhao@ipp.ac.cn
 Tel: +86-551-65591206
Tel: +86-551-65591206
 Fax: +86-551-65591270
Fax: +86-551-65591270
 Emai: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
Emai: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
 350 Shushanhu Road
350 Shushanhu Road