A research group led by Prof. FANG Xiaodong and MENG Gang from Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (AIOFM), Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) proposed a novel approach based on pulsed temperature modulation (PTM) methodology to boost the sensitivity of semiconductor gas sensors.
In this research, scientists demonstrated that in comparison with conventional isothermal measurement, PTM enabled to decouple several critical processes (physisorption, chemisorption and resistance reading) involved in molecule sensing, which possessed different temperature dependence behaviors. Under appropriate PTM, the electrical responses of a general metal oxide sensor (i.e., WO3) toward diverse vapors could be boosted by 1-2 orders of magnitude compared with the traditional isothermal test mode, approaching or exceeding the state-of-the-art chemically-sensitized WO3 sensors.
In addition, the use of micro-hotplate for PTM test could reduce the power consumption of the sensor down to 10 mW.
Sensitivity is one key parameter of semiconductor gas sensors. Conventional approach adopts ‘chemical sensitization’ strategy, including morphology control, noble metal modification, defect control, and so on. This research promised the innovation of a smart molecular sensing system with high-sensitivity, low-power, and compact size.
Link to the paper: Generic Approach to Boost the Sensitivity of Metal Oxide Sensors by Decoupling the Surface Charge Exchange and Resistance Reading Process

WO3 MEMS sensor
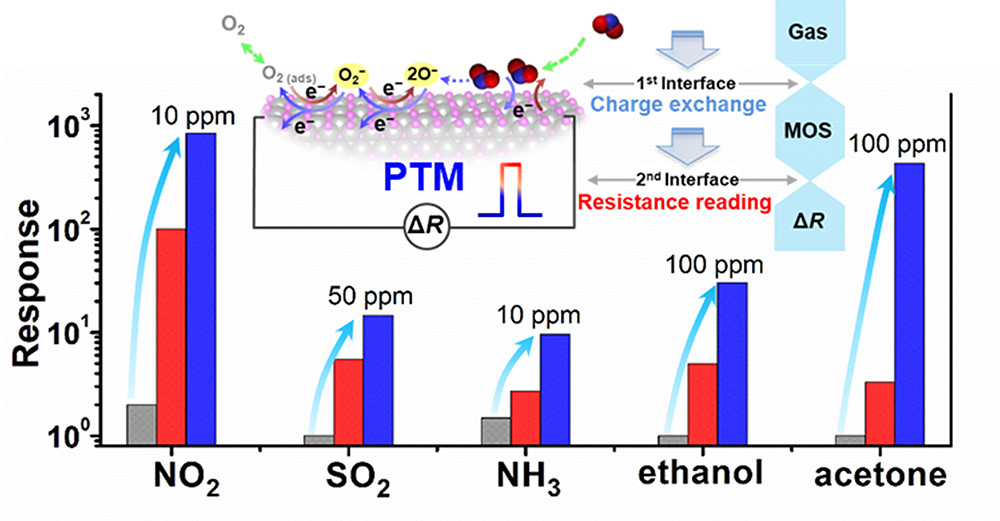
PTM (physical) sensitization
Contact:
ZHAO Weiwei
Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (http://english.hf.cas.cn/)
Email: annyzhao@ipp.ac.cn
 Tel: +86-551-65591206
Tel: +86-551-65591206
 Fax: +86-551-65591270
Fax: +86-551-65591270
 Emai: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
Emai: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
 350 Shushanhu Road
350 Shushanhu Road