Recently, scientists from Institute of Solid State Physics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) utilized valence engineering to develop three manganese oxides as electrodes with different Mn valences for high-performance capacitive desalination.
Reverse osmosis and thermal distillation are widely used to treat salt water with high salt concentration, but limited by high energy consumption and high cost.
As an alternative method, capacitive deionization (CDI) technology can remove ions through electrosorption or pseudocapacitive reaction to desalt water. However, there are few reports on manganese oxides with lower valence of Mn compared with MnO2. Hence, whether there is a difference in desalination performance in such different valence states of Mn and its internal reasons are worth exploring.
In this research, based on the high-capacity characteristic of the Faradic electrode, researchers prepared three different manganese oxide carbon compositions with different valence states of Mn by calcining MnCO3@C precursor under different atmospheres and temperatures, and then combined them with commercial activated carbon electrode to assemble an asymmetric CDI unit. Moreover, all as-prepared manganese oxides maintained the spindle-like morphology of the precursor.
The results showed that manganese oxides with divalent, trivalent and divalent/trivalent all displayed high salt adsorption capacity and corresponding high salt adsorption rates in 500 mg L-1 NaCl solution, surpassing other advanced carbon materials. Among them, MnO@C indicated the best electrosorption performance and Mn3O4@C was the worst.
The DFT calculation results proved that the valence state of manganese during Na+ absorption could bring distinct discrepancy in the spatial structure and absorption capacity.
Therefore, scientists concluded that in terms of capacity and stability, the manganese oxides with divalent (MnO@C) was more suitable than trivalent (Mn2O3@C) and divalent/trivalent (Mn3O4@C) manganese oxides for CDI desalination.
This valence engineering provided a novel way for preparing high-performance pseudocapacitive materials for capacitive desalination.
Link to paper: Pseudocapacitive desalination via valence engineering with spindlelike manganese oxide/carbon composites
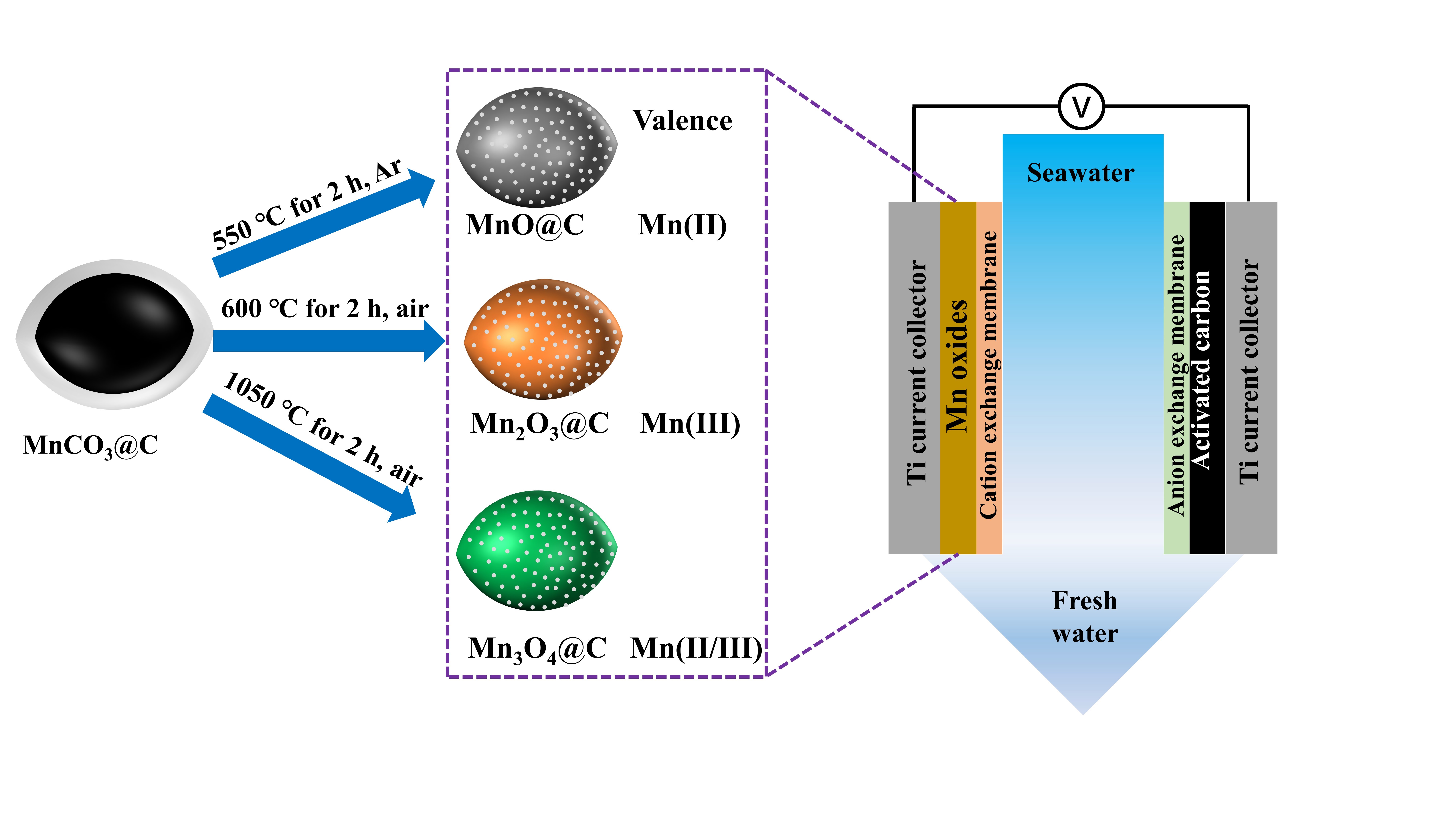
Schematic diagram of MnOx@C electrode preparation and asymmetric membrane CDI device assembly. (Image by XU Yingsheng)
Contact:
ZHAO Weiwei
Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (http://english.hf.cas.cn/)
Email: annyzhao@ipp.ac.cn
 Tel: +86-551-65591206
Tel: +86-551-65591206
 Fax: +86-551-65591270
Fax: +86-551-65591270
 Emai: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
Emai: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
 350 Shushanhu Road
350 Shushanhu Road