Recently, scientists from ASIPP Plasma Application Division found that the presence of Carbonate affect adsorption and desorption on the surface of the radionuclide in sepiolite, which could be helpful in evaluating the fate and transport of radionuclides under different geochemical conditions.
A large number of radioactive U(VI) are produced in the process of uranium mining, milling, and disposition of spent fuel from the nuclear power industry.
Prof. Xiangke Wang’s research group has extensively investigated the physicochemical behaviors of radionuclides and high efficient enrichment of radionuclides on a variety of adsorbents.
The effect of environmental factors (i.e., pH, ionic strength, humic acid and temperature) on the diffusion of radionuclides at water-mineral interfaces has been conducted by using extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectra (EXAFS).
On the base of above research, associate researcher Yubing Sun in the Wang’s groups studied the interaction mechanism between U(VI) and U(VI) with sepiolite at the molecular level by the combination of macroscopic adsorption, microscopic characterization and surface complexation modeling.
The results showed that the inner-sphere surface complexes of type-A (>SOMCO3(n-3)+) were transferred to type-B (>SOCO2M(n-1)+) as the increase of pH in the presence of carbonate.
At low pH conditions, two inner sphere complexes, including bidentate edge-sharing (E2) and bidentate corner-sharing (C2), have been demonstrated by three surface complexation modelings (CCM, DLM, TLM) and spectroscopic techniques (e.g., XPS, EXAFS).
This study will establish the foundation for the further investigation of physicochemical behaviors of radionuclides at water-mineral interfaces. This research has been recently published in Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta (DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2014.06.001), which is the international famous journal of geosciences.
Article links: http://authors.elsevier.com/sd/article/S0016703714004025

Schematic structure of bidentate edge-sharing (E2) and corner-sharing (C2) surface complexes on sepiolite.
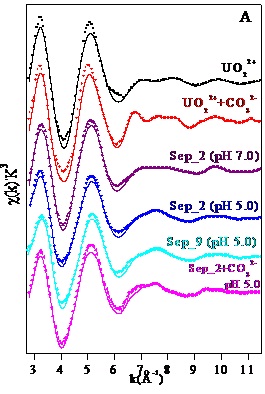
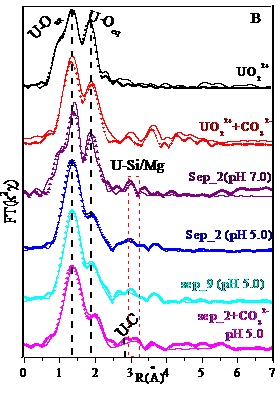
EXAFS spectra (A) and their corresponding Fourier transform (FT) (B) for U(VI)-reacted sepiolite in the absence and presence of carbonate