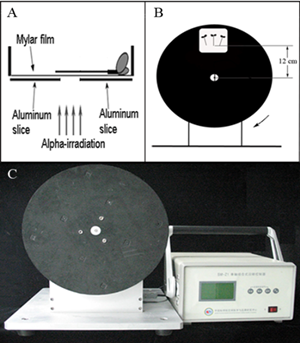
Both space radiation and microgravity have been demonstrated to have inevitable impact on living organisms during space flights and should be considered as important factors for estimating the potential health risk for astronauts. Therefore, the question whether radiation effects could be modulated by microgravity is an important aspect in such risk evaluation. Space particles at low dose and fluence rate, directly affect only a fraction of cells in the whole organism, which implement radiation-induced bystander effects (RIBE) in cellular response to space radiation exposure. The fact that all of the RIBE experiments are carried out in a normal gravity condition bring forward the need for evidence regarding the effect of microgravity on RIBE.
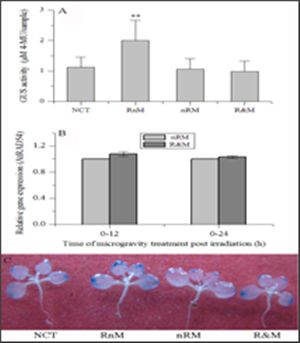
Recently, under the cooperation between professor Po Bian’s group in the Institute of Technical Biology &Agriculture Engineering and professor Min Liu’s group in China Academy of Space Technology, the modulation of modeled microgravity on radiation induced bystander effects have been found, and the results showed that the modeled microgravity inhibited significantly the RIBE-mediated up-regulation of expression of the AtRAD54 and AtRAD51 genes, generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and transcriptional activation of multicopy P35S:GUS, but made no difference to the induction of homologous recombination by RIBE, showing divergent responses of RIBE to the microgravity conditions. The time course of interaction between the modeled microgravity and RIBE was further investigated, and the results showed that the microgravity mainly modulated the processes of the generation or translocation of the bystander signal(s) in roots.
The result has been published in Mutation Research. The link to the paper:
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0027510715000214