It is well known that laser absorption spectroscopy sensors have unique advantages for fast, self-calibration, highly sensitive, nonintrusive and in situ quantification without any sample preparation. So this kind of sensors enjoys extensive applications in environmental monitoring, medial diagnostics and industrial process control.
From Beer–Lambert absorption law, detection sensitivity by absorption spectroscopy is improved with molecule absorption path length. Generally speaking, sensitive detection scheme is achieved with a traditional multipass cell.
However, for compact Herriott configuration designed conventionally, the number of light passes inside the cell is limited by the overlapping of light spots on cell mirrors through limitation of achievable optical path length within a compact cell size. As a consequence, absorption spectroscopy sensors which are compact, handheld and highly sensitive are restricted.
To shed on the problem mentioned above, a study team led by Prof. GAO Xiaoming from Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (AIOFM) developed a modified kind of laser absorption spectroscopy gas sensor which was a joint design of novel compact Dense-Pattern Multi-Pass Cell (DP-MPC) and a fiber-coupled distributed feedback diode laser.
This new design entitled “Highly Sensitive Detection of Methane by Near-infrared Laser Absorption Spectroscopy Using A Compact Dense-Pattern Multi-Pass Cell” has been published in Sensors & Actuators: B. Chemical.
The modified DP-MPC consists of two 2" silver coated concave spherical mirrors being apart of 12cm from each other. With optical design and alignment, a novel dense pattern of 7 circles was configured on the mirror after laser beam passing 215 times between two spherical mirrors without spot overlapping. And an effective optical path length of 26 m was achieved with a sample volume of 280 cm3. Highly sensitive detection of atmospheric methane (CH4) was performed by DP-MPC in conjunction with a fiber-coupled distributed feedback diode laser operating at 1.653 μm. High performance with a minimum detection accurate to 100 ppb in 1 ms and a measurement accurate to < 80 ppb have been achieved by using wavelength modulation spectroscopy approach.
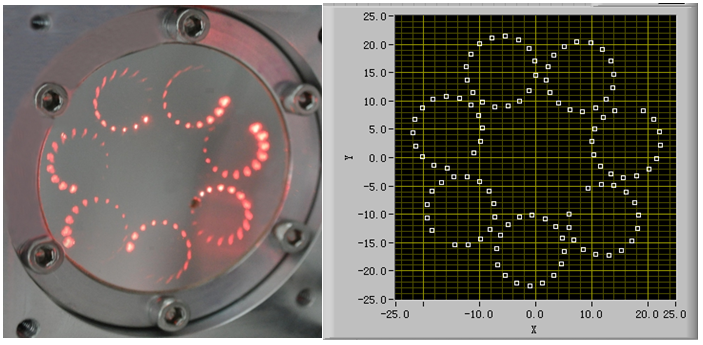
Beam Pattern Visualized Using A Red Diode Laser Beam (left) and Software Simulated Pattern (right) (Imaged by Prof LIU Kun)

Ambient CH4 Concentration Variation During Two Days Continuous Measurements (Imaged by Prof LIU Kun)
DP-MPC, being compact, wavelength-independent and with low cost, can be applied as a powerful new tool in laser-based sensing, particularly in gas sensing .
The work was supported by the grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Youth Innovation Promotion Association of CAS.
Contact:
Prof. GAO Xiaoming, Ph.D Principal Investigator
Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics,Chinese Academy of Sciences
Hefei, Anhui 230000, China
Tel: 0551-65591534
E-mail:xmgao@aiofm.ac.cn