More recently, a new progress on hierarchical microsphere with controllable surface area and porosity has been made for highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells by the associated research team led by Prof. HU Linhua in Institute of Applied Technology, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, CAS and Prof. DAI Songyuan in Renewable Energy School, North China Electric Power University. This work was reported by the famous Willy website Material Views.
An optimized configuration of TiO2 microspheres in photoanodes is of great importance to prepare highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs). In this work, TiO2 microspheres with tunable diameter, pore size, and porosity are synthesized by subtly adjusting the synthesizing conditions, including ratios of deionized water, ammonia, and ethanol, respectively. TiO2 microspheres are obtained with large pore sizes and a high porosity without sacrificing specific surface areas. As confirmed by the TEM mapping (Fig 1), dye-loading ability and electrolyte diffusion resistance, the large mesopores and the high porosity of the TiO2 microspheres can improve dye adsorption and facilitate electrolyte diffusion, giving rise to a high light-harvesting and electron collection efficiency. By modifying the interconnection and the external pores of the microspheres photoanode, a high efficiency of 11.67% is achieved for a DSSC based on the most potent TiO2 microspheres (Fig. 2). These parameters are both critical for the future preparation of high-efficiency DSSCs with TiO2 microspheres as photoanodes.
This work was supported by the National Key Basic Research Program of China and National High Technology Research and Development Program of China.
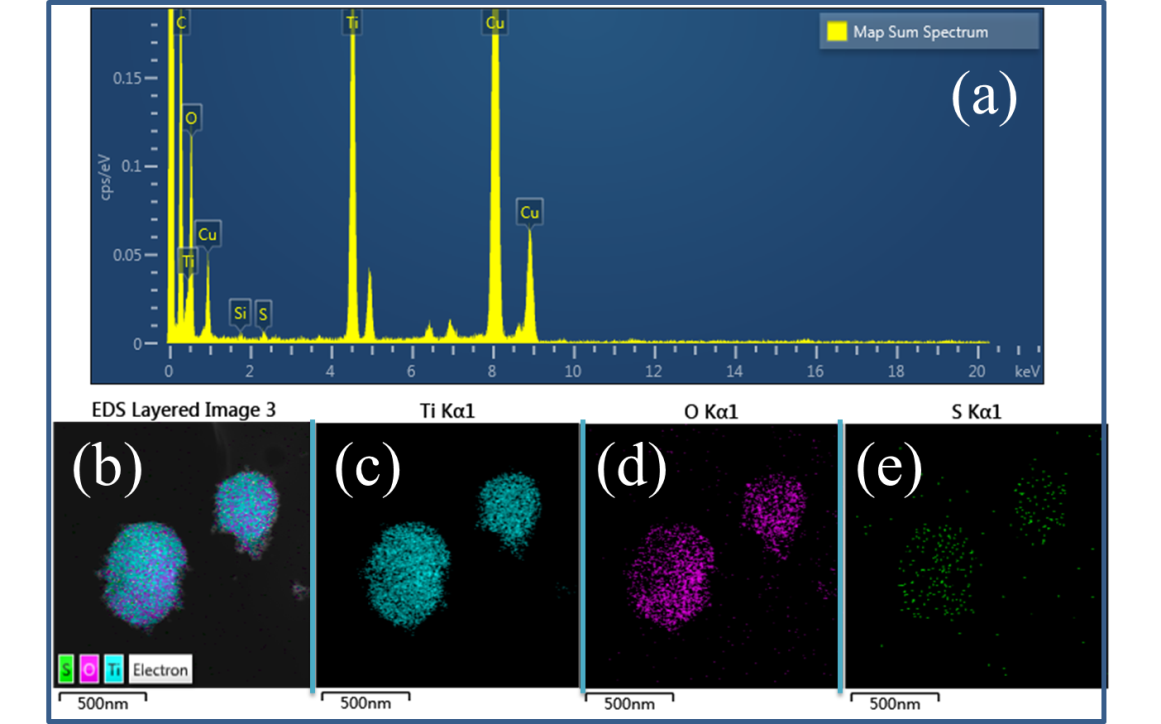
Fig.1
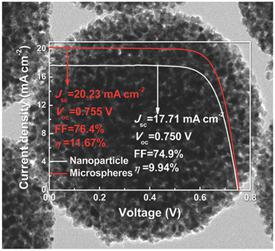
Fig.2