
A research team led by Prof. CHU Yannan from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, has conducted research on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in esophageal cancer organoids and discovered a gaseous biomarker of cancer cells.
The research results were published in the Analytical Chemistry (ACS) and were selected as the supplementary cover.
Human metabolic VOC gas biopsy and traditional Chinese medicine olfactory diagnosis use odor components to detect cancer. These methods are safe, non-invasive, convenient, and highly acceptable, making them a key focus in non-invasive tumor screening. While clinical studies have identified characteristic VOCs in esophageal cancer patients, in vitro cell experiments are needed to determine whether these VOCs originate directly from cancer cell metabolism and to clarify their metabolic mechanisms.
To address this, the team used both esophageal cancer cells and normal cells. Beyond conventional 2D monolayer culture, they also constructed 3D cell spheroids and organoids. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) non-targeted analysis was performed to compare VOCs released during cell metabolism. The results showed that across monolayer, spheroid, and organoid cultures, cancer cells released significantly higher levels of 2-methylbutanoate than normal cells. Transcriptome analysis suggested that the upregulation of ethyl 2-methylbutyrate may be linked to protein degradation and absorption pathways.
This work not only identifies VOC markers for esophageal cancer cells but also provides target molecules for studying cancer cell metabolism, offering a cellular experimental basis for the development of non-invasive screening and rapid detection technologies for esophageal cancer.
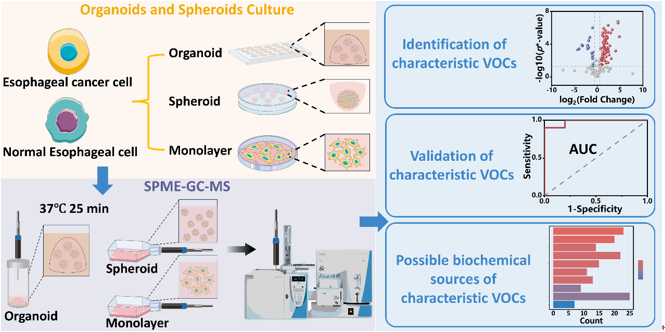
Schematic diagram of esophageal cancer cell identification research process (Image by GE Dianlong)

Supplementary cover (Image by GE Dianlong)