
Recently, a research team led by Prof. WANG Zhenyang from the Institute of Solid State Physics, the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, developed two interfacial regulation strategies to improve the stability of silicon–carbon composite anodes for lithium-ion batteries. The team proposed a laser-directed covalent bonding strategy and a hierarchical dual-coating regulation strategy, both of which effectively suppressed interfacial failure induced by volume expansion and significantly enhanced the cycling stability and electrochemical performance of the batteries.
The results were published in Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials and Composites Part B: Engineering.
Silicon-based anodes are promising candidates for next-generation lithium-ion batteries due to their high theoretical capacity, but their practical application is limited by severe volume expansion and unstable interfaces during cycling.
To address this challenge, the team proposed two interface-engineering strategies. One is a laser-directed covalent bonding strategy, which constructs robust Si–N–C bridges between silicon suboxide nanoparticles and nitrogen-doped laser-induced graphene, significantly improving interfacial stability and long-term cycling performance. The other is a hierarchical dual-coating strategy based on polyaniline and laser-induced graphene, which simultaneously enhances solid electrolyte interphase stability and relieves mechanical stress.
As a result, the optimized silicon–carbon composite anodes exhibited greatly improved cycling stability and electrochemical performance, maintaining high capacity after 1000 charge–discharge cycles at high current density.
These studies offer new strategies for developing long-life, high-energy-density lithium-ion batteries, according to the team.
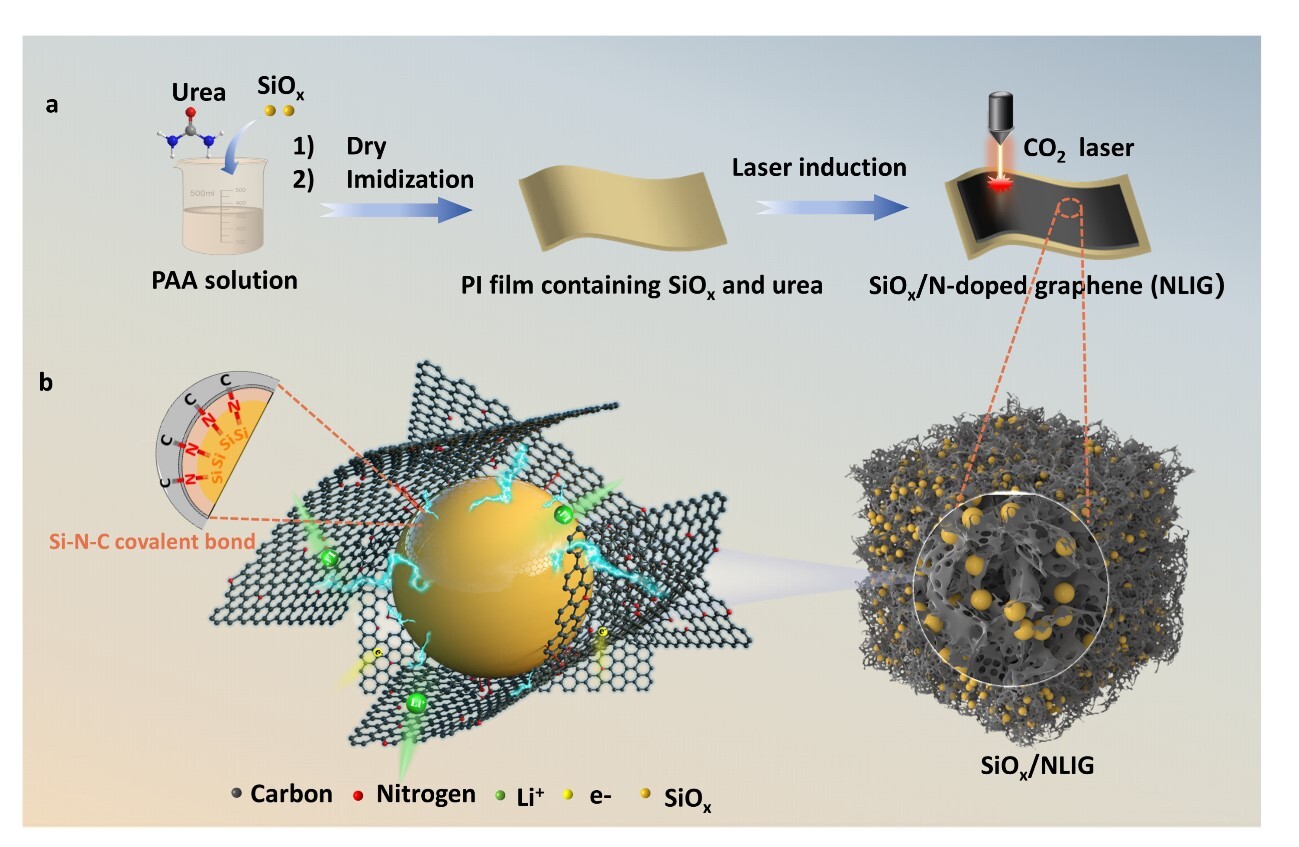
Schematic illustration of the preparation process and lithium storage mechanism of SiOx/nitrogen-doped laser-induced graphene composite materials. (Image by LI Nian)