
Recently, a team led by Prof. WU Zhengyan from Institute of Intelligent Machines, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science developed a novel Z-scheme photocatalyst to deal with contaminants in water.
In a study published in the journal Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, Prof. Wu and his doctoral student YANG Pengqi described how they used hydrothermal method to fabricate the Z-scheme photocatalyst, named CTQDs/BWO, which was designed to enhance photocatalytic efficiency.
As quantum effect dramatically promoted the transfer of charge-carriers in the interface of BWO and CTQDs, this photocatalyst exhibited much higher photoinactivation efficiency of E. coli and photodegradation efficiency of TC compared to the pure BWO under the visible light.
In recent years, rapid industrialization has caused increasingly severe environmental pollution. Antibiotics and microbiological contamination in water have become major threats to human health and critical risks to ecosystem security worldwide. Therefore, an effective treatment approach has become an urgent task for elimination of bacterial and antibiotic contamination from the watery environment at present.
This study opened up a new route to design high-efficiency Z-scheme photocatalysts and exhibited a promising prospect for practical application.
This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China, the Science and Technology Service Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the Key R&D Program of Ningxia Province.
Link to paper: Kinetics, reaction pathways, and mechanism investigation for improved environmental remediation by 0D/3D CdTe/Bi2WO6 Z-scheme catalyst
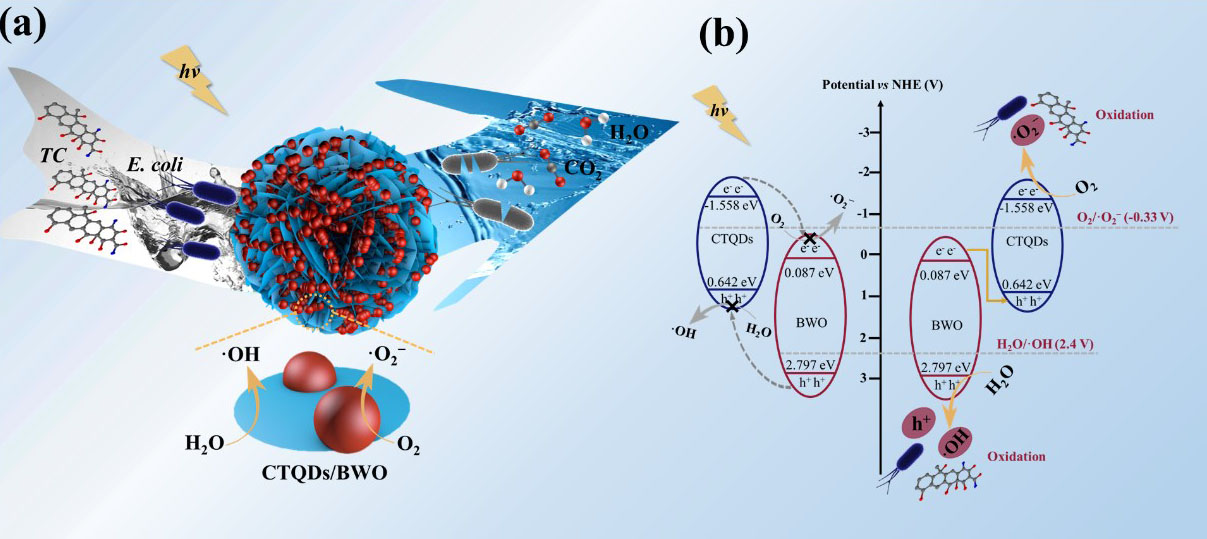
Schematic illustration of photocatalytic mechanism. (Image by YANG Pengqi)
Contact:
ZHAO Weiwei
Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (http://english.hf.cas.cn/)
Email: annyzhao@ipp.ac.cn