
Although immune checkpoint blockade has achieved great success in cancer treatment, its efficacy in breast cancer is limited. Therefore, the identification and evaluation of novel prognostic biomarkers in the immune microenvironment will be very helpful for immunotherapy-based breast cancer treatment.
Recently, the research group led by Prof. YANG Wulin and Prof. WANG Hongzhi from the Institute of Health and Medical Technology, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), identified a novel immune-related therapeutic target, which is called N-formyl peptide receptor (FPR3), in the tissue microenvironment of breast cancer. They reported their works in the journal Frontiers in Pharmacology.
In this study, researchers first used bioinformatics to study gene expression data in the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) to investigate the tumor microenvironmental factors related to breast cancer. Later they analyzed the result with Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis (WGCNA) to identify a gene functional module associated with tumor immune score.
Although protein-protein interaction (PPI) network analysis showed that many immune checkpoint genes were enriched in the immune-related functional module, “star” immune checkpoints, such as CTLA4, PDCD1, were not strongly associated with the prognosis of breast cancer. Researchers found that, among the functional modules relating to immune score and associating with an unfavorable prognosis, FPR3, a G-protein-coupled receptor necessary for neutrophil activation, is the only gene that is up-regulated.
"Genome enrichment analysis showed that the up-regulation of FRP3 could synergize with the activation of multiple carcinogenic pathways,” concluded YANG Wulin, a scientist of medicine, "it turned out to be a key immune-related biomarker for predicting, and could contribute to the development of new therapy for breast cancer.”
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Innovative Program of Development Foundation of Hefei Center for Physical Science and Technology, and the foundation of Anhui Province Key Laboratory of Medical Physics and Technology.
Link to paper: Identification of FPR3 as a Unique Biomarker for Targeted Therapy in the Immune Microenvironment of Breast Cancer
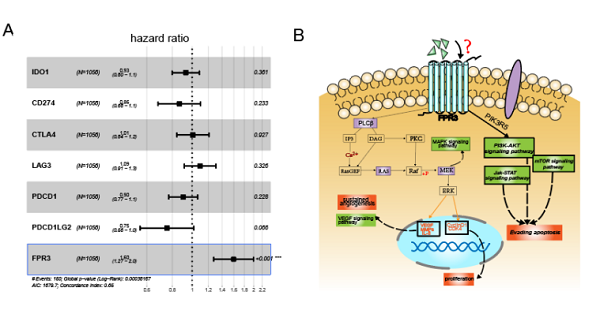
A model diagram was proposed that FPR3 may be involved in the occurrence and progression of cancer via G protein coupled signaling.(Image by LIU Yu)
Contact:
ZHAO Weiwei
Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (http://english.hf.cas.cn/)
Email: annyzhao@ipp.ac.cn