
Atmospheric conditions vary significantly in terms of the temporal and spatial scales. The purpose of atmospheric correction based on radiative transfer model is to remove the atmospheric radiative effect on remote sensing images, but it is always limited by the difficulty in obtaining atmospheric parameters that match image in terms of the temporal and spatial scale.
To retrieve the surface reflectance, scientists from Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed a method to remove the influence of the atmosphere and the adjacency effects recently, and thus to achieve the real reflectance of ground objects.
The relevant research was published in Remote Sensing.
"What we suggested in this experiment is called synchronization atmospheric correction (Syn-AC) method," said XU Lingling, first author of the paper. "We used it to retrieve synchronous atmospheric parameters from SMAC."
They tried it on multi-spectral remote sensing images of Gao Fen Duo Mo (GFDM), the first civilian high-resolution remote sensing satellite equipped with the Synchronization Monitoring Atmospheric Corrector (SMAC), and did synchronous atmospheric correction successfully.
Aside from that, they conducted the synchronous field-measured experiments to test the performance of Syn-AC.
Scientists selected six images under different atmospheric conditions, which are from three radiometric calibration sites (Dunhuang, Songshan and Baotou), to conduct atmospheric correction experiments. They compared visual effects before and after atmospheric correction.
They also compared the average reflectance of the selected targets in the surface reflectance image of Syn-AC with the field-measured reflectance values.
The results indicated that the visual effects of corrected image were improved with the blurring effect removed, and the real features of ground objects were effectively recovered.
Atmospheric correction based on synchronous atmospheric parameters could promote the quantitative application of GFDM satellite data.

Figure 1 Visual effects of the images before and after Syn-AC (Image by XU Lingling)
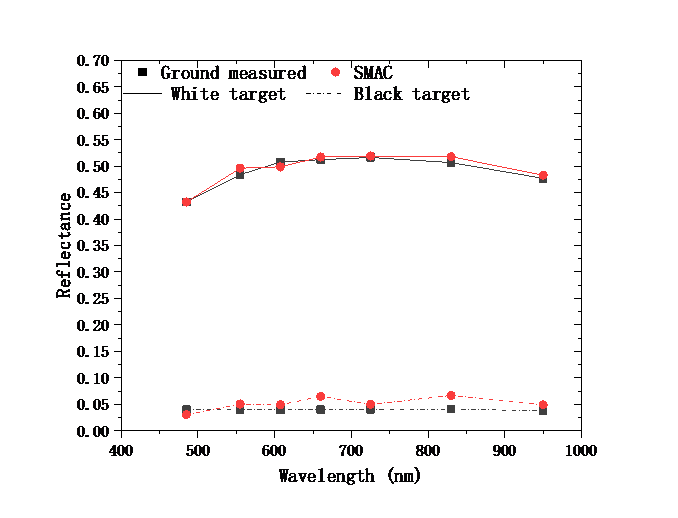
Figure 2 Comparison between the retrieved reflectance after Syn-AC and the field-measure values of the white and black targets in the Songshan site. (Image by XU Lingling)