
A team led by Prof. XU An from Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of Chinese Academy of Sciences revealed the mutagenicity of α-endosulfan in Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) germ cells in a recent study.
The result was published in Environmental Science & Technology.
Endosulfan, featured on environmental persistence, high toxicity and bioaccumulation is a widely used broad-spectrum organochlorine pesticide. Epidemiological studies and animal studies have shown that endosulfan exposure compromises reproductive system, and disturbs development of offspring. However, the potential mechanisms of the reproductive toxicity induced by endosulfan remain poorly explored.
In this study, researchers developed a high-throughput technique for identifying gene mutations in germ cells using next-generation sequencing.
They found that low dosages of α-endosulfan had a negligible impact on reproductive capacity of C. elegans, whereas 1 μM α-endosulfan significantly elevated the mutation frequencies of nonexposed progeny.
Further analysis of genome-wide mutation patterns revealed that a-endosulfan induced A:T→G:C base substitutions and clustered mutations in germ cells, which was modulated by translesion synthesis polymerase η.
These observations demonstrated that α-endosulfan preferentially elicited bulky O4-alkyl-dT DNA lesions in germ cells, followed by error-prone bypass of the lesions through pol η.
The results also suggested that germ cell mutagenicity should be a necessary consideration for health risk assessment of environmental pollutants such as persistent organic pollutants (POPs), where next-generation sequencing technology provided a promising method for such analysis.
The research has been supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (22006149).
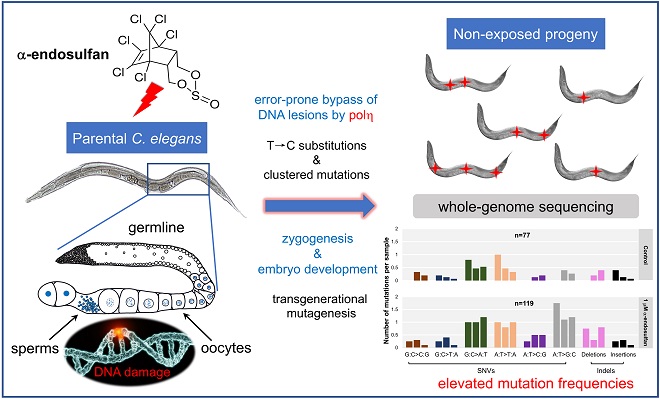
α-endosulfan elicits A:T→G:C substitutions in non-exposed offspring of C. elegans, which is modulated by translesion synthesis polymerase eta. (Image by CAO Zhenxiao)