
Recently, Prof. HUANG Qunying’s team from Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) developed a novel silica-based adsorbent for the highly selective separation of strontium (Sr) from acidic medium, collaborating with Prof. NING Shunyan's team of South China University.
The results were published in Journal of Hazardous Materials.
Radioactive strontium, known as 90Sr, is a concern because it's highly toxic both radiologically and biochemically. When dealing with high-level liquid waste (HLLW) through a process called vitrification, the heat released from the decay of 90Sr can cause issues. This heat can destabilize the material it's contained in, potentially leading to the release of other radioactive substances. However, 90Sr can also be repurposed as a special radioactive or heat source, which can help reduce the volume of waste needing disposal and lower overall costs.
To address the above issues, the team developed a novel porous adsorbent called CEPA@SBA-15-APTES. This adsorbent is made by modifying mesoporous silica to selectively separate Sr. They studied how this adsorbent behaves when exposed to different environments by using Sr stable nuclides. They found that the adsorption reached equilibrium in 30 minutes in a solution with a low concentration of nitric acid (HNO3) and in just 5 minutes in a solution with a higher concentration of HNO3.
Importantly, the adsorbent demonstrated excellent selectivity for Sr in 3 M HNO3 simulated HLLW with the separation factor exceeding 90. The mechanism behind Sr adsorption differs depending on the acidity of the solution: ion exchange occurs in solutions with low HNO3 concentration, while coordination takes place in solutions with higher HNO3 concentration.
This study developed a novel material for the efficient separation of strontium, which is a reference for the selective separation and recovery of radionuclides.
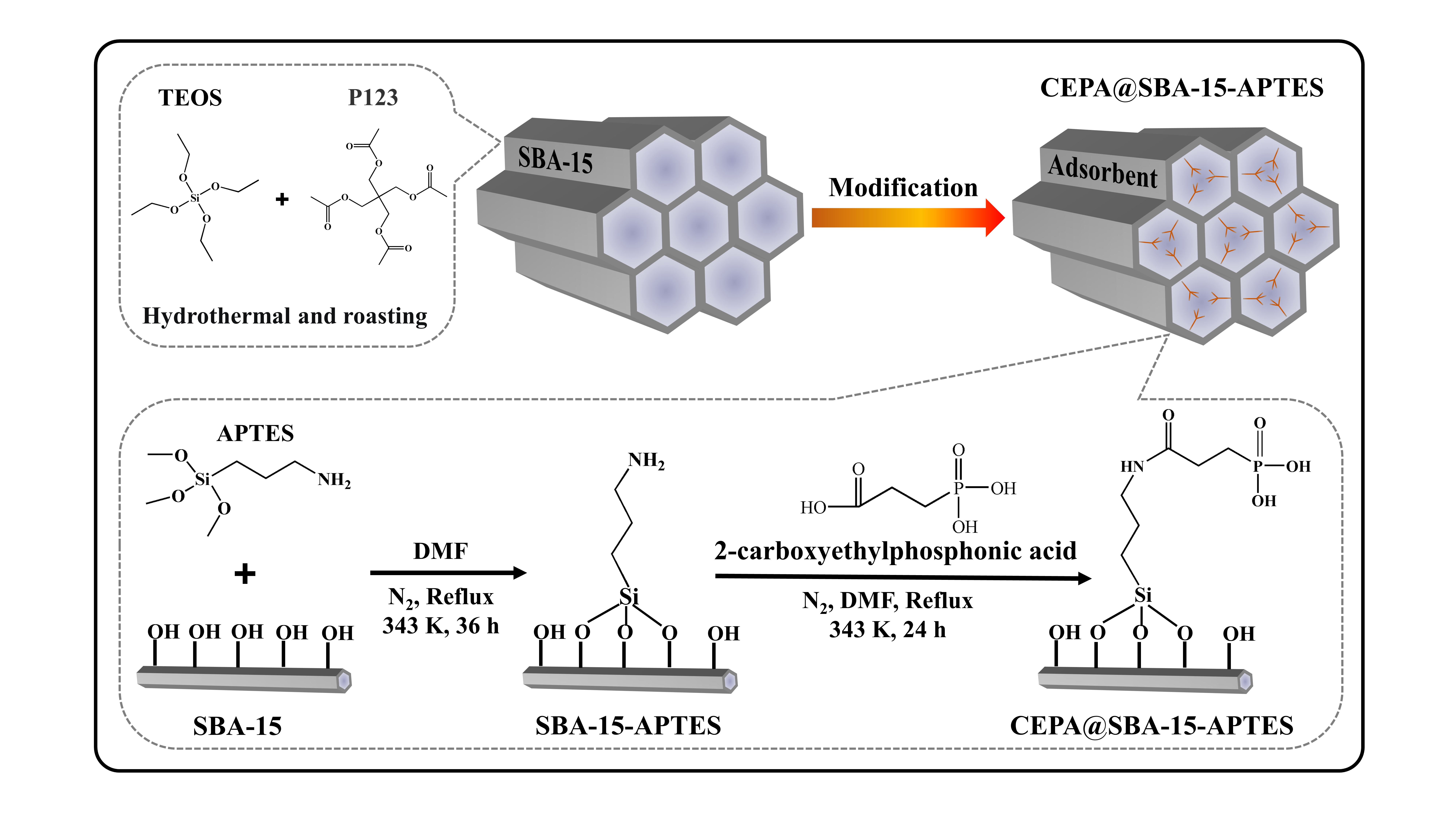
Figure 1 Schematic illustration of CEPA@SBA-15-APTES preparation process. (Image by ZHANG Shichang)

Figure 2 Adsorption selectivity: (a) Effect of four competing ions on Sr adsorption in 10-6 M HNO3 solution; (b) Adsorption of different metal ions in the HNO3 solutions. (Image by ZHANG Shichang)