
Recently, the research team led by Professor WU Lifang from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, has developed an efficient in vitro regeneration protocol for Eucommia ulmoides Oliv.
The research results were recently published in Frontiers in Plant Science.
E. ulmoides is a distinctive multifunctional tree species native to China, recognized as a high-quality raw material for the development of modern traditional Chinese medicine, health products, and functional foods. Current seedling cultivation methods are inadequate to meet the breeding requirements for E. ulmoides seedlings. Hence, there is an urgent need to conduct research on advanced breeding techniques for efficient E. ulmoides seedlings.
In this study, the team developed a better method for growing E. ulmoides plants in the lab. Their approach efficiently helps the plants regenerate by growing new shoots directly and using a two-step process to help the plants grow roots.
The researchers explored how different factors like the type of growth medium, plant hormones, light intensity, and sugar levels affect the growth of buds. As a result, they were able to shorten the time needed for buds to grow and multiply to just 4 weeks, with an impressive increase in the number of buds—about 5 times more than before.
Furthermore, to address the primary challenge of inducing root formation in regenerated plants, they employed a two-step rooting technique. This method resulted in an optimal rooting frequency, significantly enhancing the quality of adventitious roots.
“The micropropagation system established in this study provides essential technical support for the conservation of superior E. ulmoides germplasm, large-scale seedling production, and future cultivar improvement,” said Dr. HOU, corresponding author of the study.
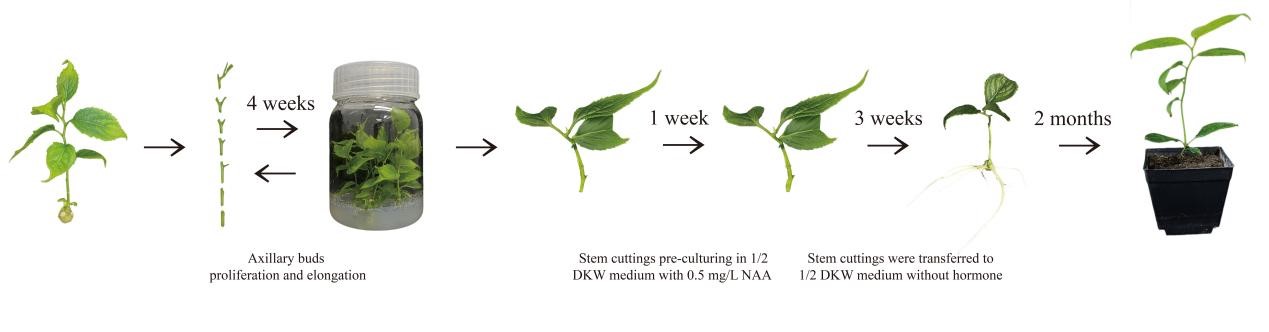
Diagram of establishing a efficient regenerative system for E. ulmoides (Image by WANG Dacheng)