
Researchers from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, have developed a self-attention-based neural network model for rapid prediction of radiation shielding designs in space reactors.
The findings were published in Nuclear Engineering and Design.
Micro and small reactors are compact, safe, and low-carbon energy sources. However, their lightweight shielding design faces challenges such as limited space, weight constraints, and complex material configurations. Traditional methods like Monte Carlo simulations are accurate but time-consuming and inefficient for rapid optimization.
In this study, researchers focused on space reactors and developed an intelligent model to help design radiation shielding more quickly and efficiently. This model is based on "self-attention neural network," which can learn patterns and make accurate predictions. To train the model, the team used data generated by SuperMC — a powerful simulation tool developed by the institute — which calculates how radiation interacts with different shielding materials.
By feeding the model information like shielding weight and radiation levels, it can quickly suggest effective shielding designs. Tests showed that the model' s results are very close to traditional methods, with less than 3% difference, but it works much faster.
This research provides an innovative approach to shielding design optimization for micro and small reactors.
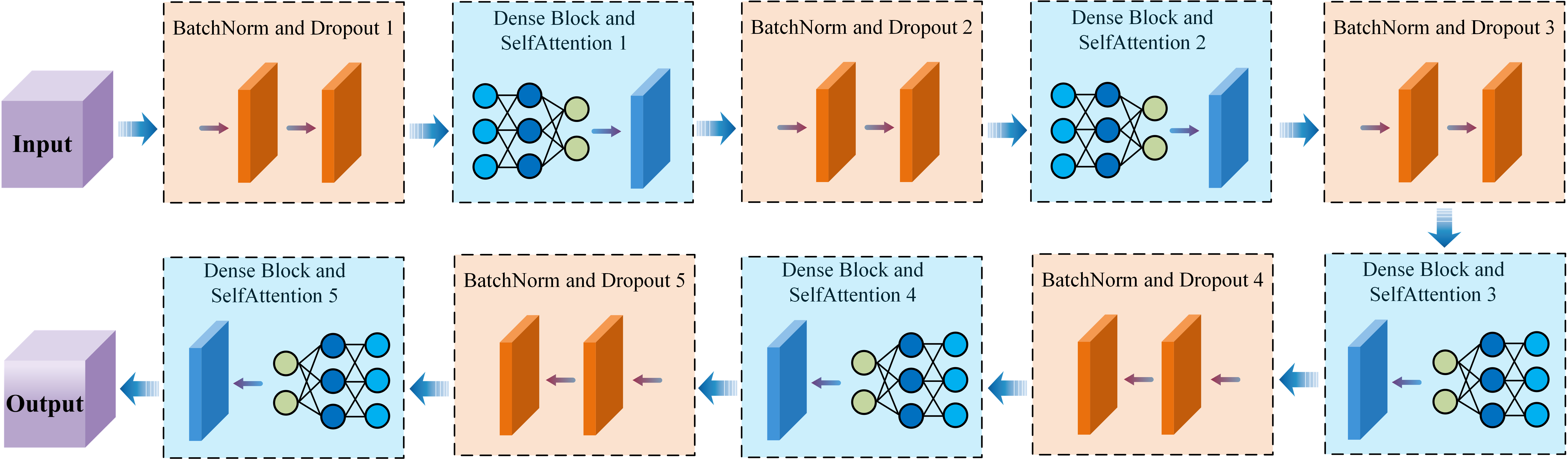
Neural network model diagram(Image by CHEN Qisheng)