
Researchers at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, have developed advanced robotic technologies to support the assembly and maintenance of future fusion reactors.
Their work, published in IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics and Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, addresses the critical challenge of operating heavy robotic arms with extreme precision in complex and hazardous environments.
A novel robotic joint was designed for heavy-duty robotics. By removing the sun gear from the traditional planetary gearbox, researchers created additional space for power and control cables without compromising compactness. The joint’s new three-stage transmission mechanism achieves an ultra-high reduction ratio of 13,806:1, delivering torque up to 139kNm with a low backlash of 4.86arcmin. Tests confirmed its strength, precision, and reliability, making it ideal for handling massive in-vessel components.
To solve the problem of precise peg-in-hole assembly in radiation environments, inspired by human hand–eye coordination, the team developed a deep reinforcement learning based method that integrates signals from a 2D camera and a force/torque sensor. The proposed system reached sub-0.1 mm accuracy, even without advanced 3D vision.
In terms of environmental perception, the researchers introduced TCIPS, a Transformer-based model that segments 3D point cloud data into basic geometric primitives such as planes, spheres, and cylinders. By capturing long-range spatial relationships and improving boundary detection, TCIPS enhances robot navigation in cluttered reactor settings.
Together, these innovations mark a significant step toward building intelligent, heavy-duty robotic systems capable of carrying out complex and high-risk maintenance tasks in future fusion power plants.
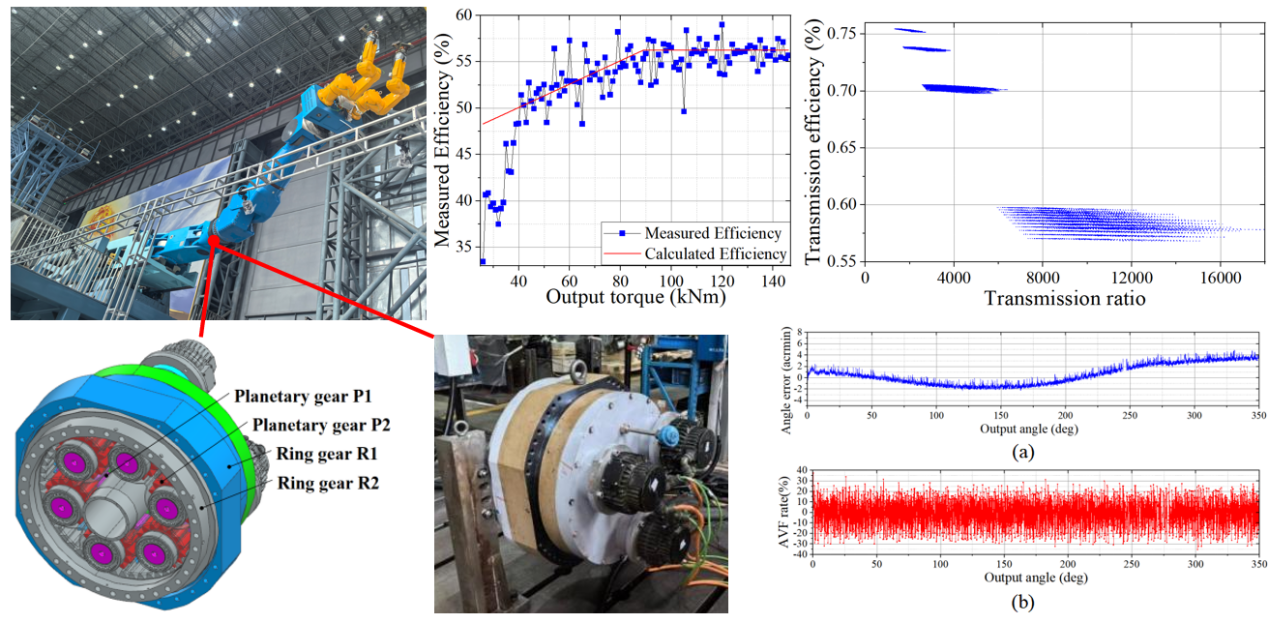
Heavy-Duty Robotic Arm Joint and Parameter Optimization (Image by CHENG Yong)