
In natural ecosystems, soundscapes are made up of animal sounds, environmental noises, and human activity. Because different animals vocalize at different times and frequencies, researchers can study audio recordings to understand local biodiversity. Discriminative machine learning is often used to analyze how biodiversity changes over time and across regions. However, in ecosystems with many species and complex sounds, it is still difficult to accurately identify species and measure biodiversity, which limits the wider use of soundscape analysis in ecological monitoring.
A team led by Prof. LIU Fanglin from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a novel method based on generative models for ecological soundscape analysis.
The results were recently published in Methods in Ecology and Evolution.
The method uses generative adversarial networks (GANs) to learn the underlying patterns of sound signals from real spectrograms, and then applies this knowledge to reconstruct species-specific vocal components, generating sounds that closely mimic natural soundscapes.
Unlike conventional discriminative models, this generative strategy captures the intrinsic structures and hidden features of the acoustic space such as the frequency ranges, temporal patterns and energy intensities of animal calls, thereby enabling more precise separation of target sound sources, effective removal of environmental noise and clearer restoration of bioacoustic events.
This work expands the theoretical and methodological boundaries of biodiversity and soundscape analysis, providing new ways for automated ecosystem monitoring and ecosystem health assessment.
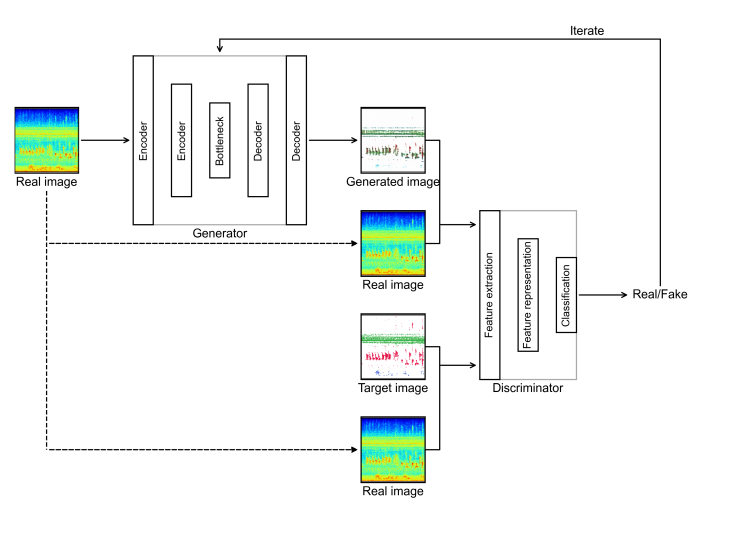
Schematic of the generative adversarial network (GAN) architecture. (Image by Wang Mei).
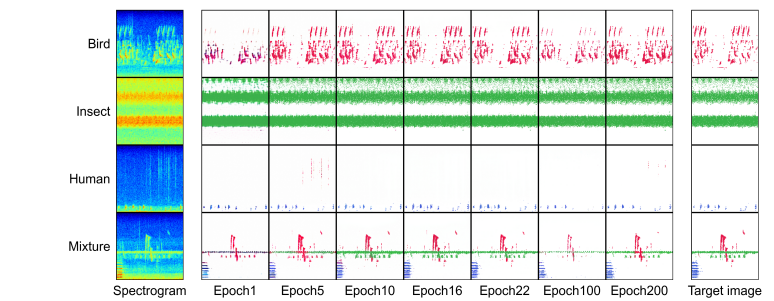
Visual comparison of images generated by the community generative adversarial network (GAN) model. (Image by Wang Mei).