
Recently, the research groups led by Prof. ZHANG Qingli and Prof. JIANG Haihe from Hefei institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have jointly developed a high-symmetry gradient-doped Nd:YAG laser crystal designed for dual-end pumping configurations. This innovation significantly mitigates thermal effects and enhances laser performance.
The relevant results were published in Optics Express.
In solid-state laser technology, the thermal effect of the laser gain medium is one of the technical bottlenecks that limit the improvement of laser performance. The previous research showed that gradient concentration crystals could effectively improve the thermal effect.
In this study, the team designed high-symmetry gradient-concentration Nd:YAG crystal rods by bonding two identical gradient-doped rods. In these rods, the dopant concentration gradually decreases from the center to both ends, forming a higher-doped center and lower-doped ends.
When operated at the same pump power, the high-symmetry gradient-doped Nd:YAG crystal showed a far smaller temperature difference between its center and ends—about only one-third of that in a conventional uniformly doped crystal. It achieved a much higher output, reaching over 14 W, with its efficiency boosted by more than half. Even at moderate output levels, it maintained a noticeably better beam quality, producing a more stable and symmetrical laser beam than the uniformly doped crystal.
This work shows that high-symmetry gradient-concentration laser crystal is expected to provide an outstanding gain media for dual-end pumping.
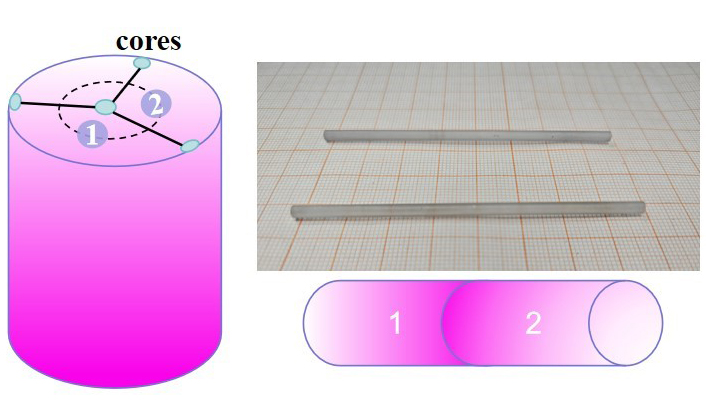
Fig. 1. High symmetry crystal rods synthesis diagram and crystal rods. (Image by DOU Renqin)
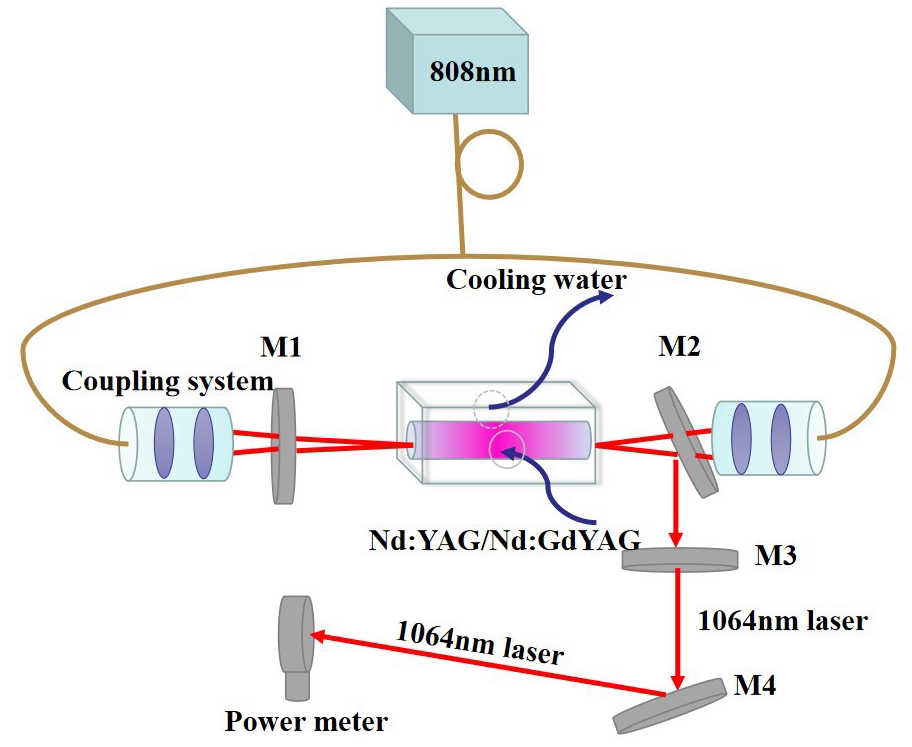
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of laser experimental setup for LD end-pumped (Image by DOU Renqin)