
A research team led by Prof. LIU Haiqing at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, has carried out a comprehensive analysis of uncertainty propagation in free-boundary plasma equilibrium reconstruction.
Their findings, published in Nuclear Fusion, offer new insights into how input measurement errors influence the accuracy of tokamak equilibrium calculations.
Plasma equilibrium reconstruction is essential for tokamak operation, providing the basis for plasma control, stability evaluation, and the interpretation of diagnostic data. However, uncertainties in experimental inputs can significantly affect the reliability of these calculations.
In this study, researchers systematically map how such uncertainties translate into variations in key equilibrium parameters. They find reliable reconstruction requires core diagnostic inputs—such as magnetic probe measurements and the toroidal field—to remain within a controlled accuracy range. Improved precision in midplane and X-point position data can further enhance reconstruction quality.
The analysis shows that different parts of the plasma respond differently to input uncertainties. The core q-profile is most affected by the toroidal field and initial plasma current, while the edge q-profile is highly sensitive to the X-point and outer midplane positions. Plasma shape accuracy is similarly influenced by uncertainties in these boundary-related measurements.
The team also found that the toroidal magnetic field exhibits strong sensitivity near the midplane, whereas uncertainties in other regions remain comparatively low. Global parameters such as beta and plasma volume are mainly affected by midplane position and current-related inputs. The magnetic axis position is influenced by uncertainties in X-point and strike-point coordinates.
"Our study provides a useful reference for refining diagnostic setups and improving the robustness of plasma control strategies," added Prof. LIU.
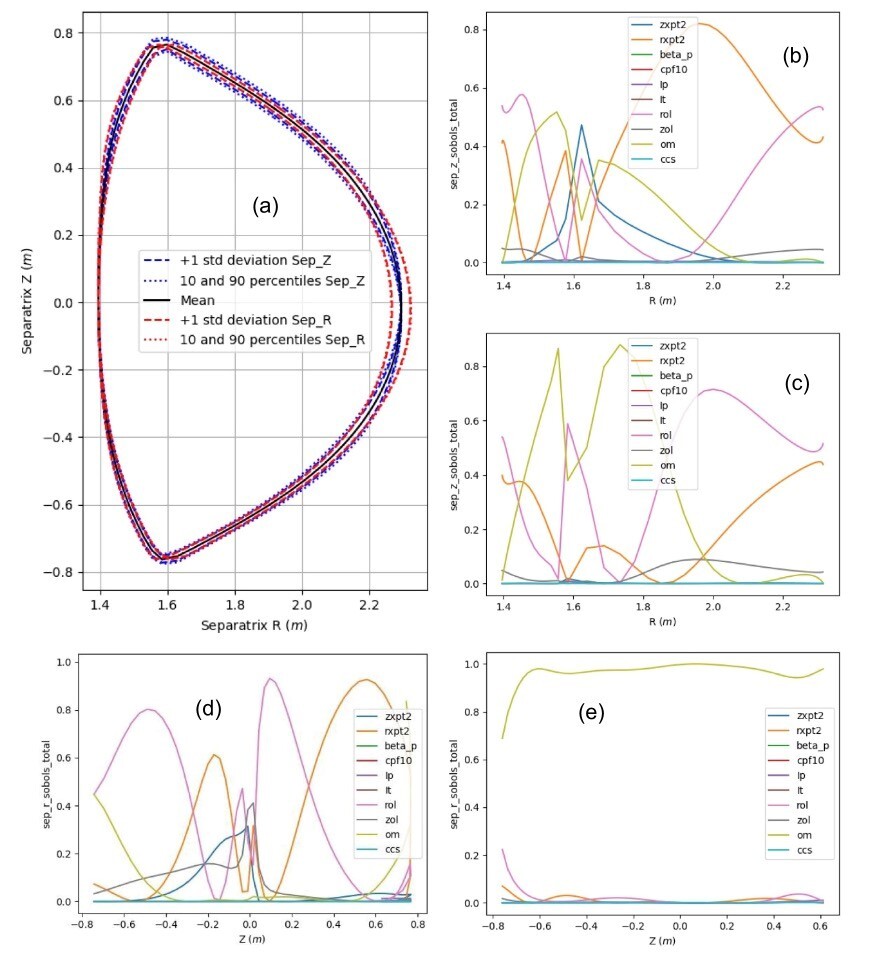
The uncertainty quantification of the separatrix (a); the sensitivity analysis of the upper (b) and lower (c) half of the separatrix Z-coordinate; the sensitivity analysis of the left-side (d) and right-side (e) half of the separatrix R-coordinate. (Image by LIU Haiqing)