
Recently, a research group led by Prof. XIE Pinhua from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, developed a highly sensitive multi-pass thermal dissociation cavity ring-down spectrometer (PNs/ANs-TDCRDS) to accurately quantification in realtime under gas and particle phase organic nitrates.
The research results were published in Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical.
Gas-phase organic nitrates (PNs and ANs) can readily transform into particle-phase organic nitrates through gas–particle partitioning or further oxidation. Accurate and simultaneous measurement of organic nitrates in both phases is essential for understanding key tropospheric processes, including atmospheric oxidation, O₃ and NOₓ cycling, and secondary organic aerosol formation. However, such measurements remain limited.
In this study, the team developed a sensitive, portable, and fully automated PNs/ANs-TDCRDS system integrating custom thermal dissociation inlets, an automated valve control unit, and a three-channel NO₂-CRDS detector. The new instrument effectively overcomes key technical challenges, including particle-phase adsorption interference, high-sensitivity detection, and measurement accuracy during phase switching, enabling reliable simultaneous detection of organic nitrates in both gas and particle phases.
By continuously monitoring NO₂, the system captures rapid concentration changes, significantly reducing their impact on the quantification of low-abundance PNs and ANs and minimizing switching-related measurement biases. The accuracy and stability of the switching measurement mode were further validated through consistent NO₂ measurements in both gas- and particle-phase configurations.
Laboratory evaluations and field observations conducted on Hefei Science Island demonstrated the instrument’s strong performance. The results showed that particle-phase PNs and ANs accounted for a substantial fraction at night, reaching 41% and 54%, respectively.
"Our finding provided valuable technical support and analytical tools for further research and development of PNs and ANs in gas and particle phases," said Prof. XIE.
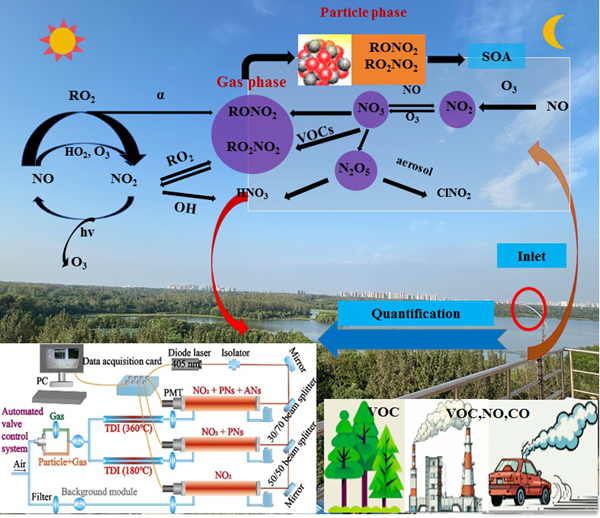
The chemical transformation process of atmospheric gas- and particle-phase organic nitrate species (Image by LIN Chuan)