
Recently, the team led by Prof. WU Zhengyan and ZHANG Jia from the Institute of Intelligent Machines of Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), designed an all-in-one nanozyme for capture, separation, and detection of copper ion (Cu2+) in complicated matrixes, achieving accurate detection of copper ions.
Relevant research results have been published in Small.
Copper is an essential trace element for the human body and an important component of agricultural fungicides. When copper accumulates to a certain concentration, it will affect human health and soil quality. In view of the important physiological role and potential hazards of copper, there is an urgent need to develop new methods for the detection of copper ions in complex systems.
In this research, the team developed an all-in-on nanozyme based on ZnPB NP (zinc-doped Prussian blue nanoparticles).
The signal generated by ZnPB NPs exhibited a positive correlation with the copper level due to the enhanced catalase-like activity of ZnPB NPs in the presence of copper ions. Consequently, the ZnPB NPs served as a comprehensive sensor for copper ions, offering a simple yet reliable solution to detect copper.
"It can efficiently capture, separate and detect copper ions, showing good selectivity and interference resistance," said YUAN Xue, member of the team, "and can be used for the determination of copper ions in undiluted human urine and soil."
Compared with the data obtained by ICP-OES (inductively coupled plasma- optical emission spectroscopy), this method has excellent copper ion detection accuracy while significantly reducing costs.
This all-in-one nanozyme offered a viable and simply-implemented solution for people at insufficiently equipped areas and regions to monitor or evaluate copper levels associated with the health statuses of person and soil.
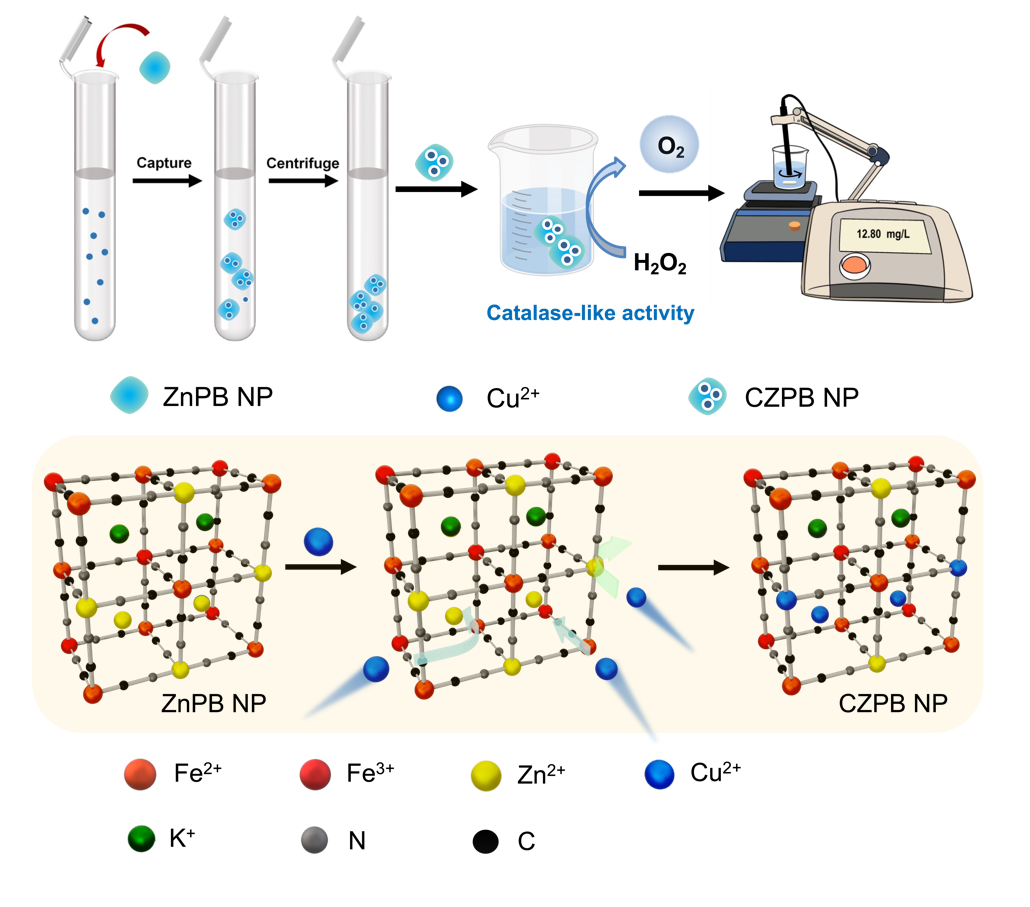
Detection of Cu2+. (Image by YUAN Xue)