
A research group led by Prof. SHENG Zhigao from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, has discovered mirror symmetry triggered chiral phonon behavior and a giant magneto-optical modulation in the two-dimensional material AgCrP2S6 with space- and time-symmetries.
The research, recently published in Advanced Functional Materials, highlights the significance of mirror symmetry in inducing chiral phonon behavior and the role of the magnetic field in modulating the magneto-optical Raman effect of phonons.
Chiral phonons are linked to phenomena such as inter-valley scattering and topological states, but they have mostly been observed in materials that break inversion or time-reversal symmetry. Their behavior in systems preserving both symmetries is still poorly understood, and past magneto-optical Raman studies have focused mainly on achiral phonons, leaving their magnetic response unclear.
In this research, using a magneto-optical Raman measurement system, the researchers observed that the Bg4 mode of AgCrP2S6 exhibits chiral phonon behavior, making the first observation of such behavior in a system with both P and T symmetries. Symmetry analysis suggests that this arises from a half-wave plate-like effect under mirror symmetry.
Magneto-Raman spectroscopy further revealed an exceptionally strong field-dependent modulation. As the field strength increased, the degree of linear polarization of the Ag5 mode significantly decreased. Bg4 mode exhibited a pronounced change while Ag5 mode responded weakly in the degree of circular polarization, underscoring the distinct and highly mode-dependent nature of the magneto-optical behavior.
"These results show that mirror symmetry plays a key role in creating chiral phonons, and they also reveal how efficiently and sensitively magnetic fields can tune Raman signals," said Prof. SHENG Zhigao. "This makes AgCrP2S6 a very promising material for future magneto-optical devices."
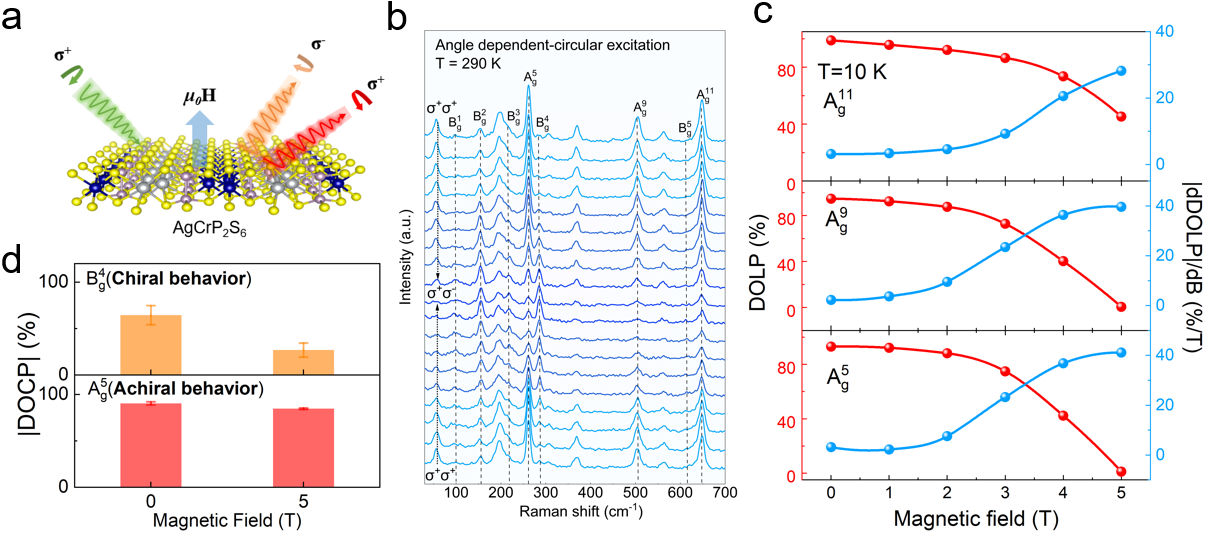
(a) Schematic illustration of the magneto-optical Raman experiment. (b) Observation of chiral phonon behavior in the Bg4 mode. (c) Magneto-optical Raman effect (linear polarization). (d) magneto-optical Raman effect (circular polarization). (Image by LI Bolin)