
Neutron, as an electrically neutral particle, has a strong penetrability and always emits secondary gamma rays during the particle collision process. The scientific and efficient scheme of shielding neutron is to select high Z (atomic number), low Z materials, and neutron absorbing materials simultaneously for combined shielding. However, lead-containing materials are restricted in application with biological toxicity.
An invention by Dr. HUO Zhipeng and his student ZHAO Sheng from the Institute of Plasma Physics, Hefei Institutes of physical science (HFIPS), Chinese Academy of Sciences solved this problem. Scientists developed a lead-free composite shielding material for neutron and gamma-ray, which featured in both high shielding performance and environmental friendliness.
The novel composite materials are named modified-Gd2O3/B4C/HDPE. To find this safe and effective composite, scientists conducted a series of intricate and comprehensive experiments to test out the possibility. They studied the shielding mechanism first, and then adopted the coupling agents to modify the surface of Gd2O3 to improve the interfacial compatibility and dispersion of Gd2O3 in the matrix.
"This is a safe and effective way to shield neutron and gamma rays," said Dr. HUO Zhipeng, a scientist focusing on radiation and environmental protection for years, "it has no threat to environment and humans as it contains no lead."
He further explained how this radiation shielding system worked. Fast neutrons collide with Gd inelastically, and collide elastically with H until they become thermal neutrons, finally, absorbed by Gd and B. Furthermore, Gd, as high Z element with superhigh absorption cross-section, has a combined function of neutron and gamma-ray absorption.
Shielding tests conducted by the Beijing Research Center for Radiation Application proved the good performance of the composite materials.
The optimal composite achieved as high as 98% neutron shielding rate with the thickness of 15 cm under Cf-252 environment. Under Cs-137 and Co-60 environment, this composite could achieve 72% and 60% gamma shielding rates with the same thickness, respectively.
Its comprehensive shielding performance is superior to conventional boron-containing polyethylene for collimating shield which applied to neutron and gamma spectrum diagnostic system of Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST). And it is expected to be promising radiation shielding material used in neutron-gamma mixed fields.
Their latest result was published on Nuclear Materials and Energy.
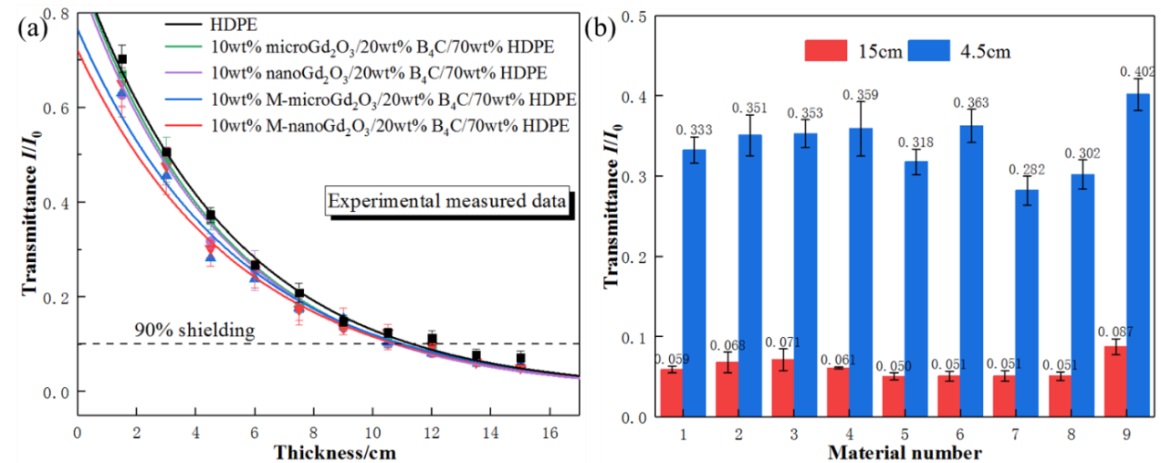
Fig. 1. (a) Comparison of neutron transmittance between nano/micro composite materials and modified nano/micro composite materials (b) Comparison of neutron transmittance of various composite materials at thickness of 4.5 cm and 15 cm (Image by HUO Zhiping)
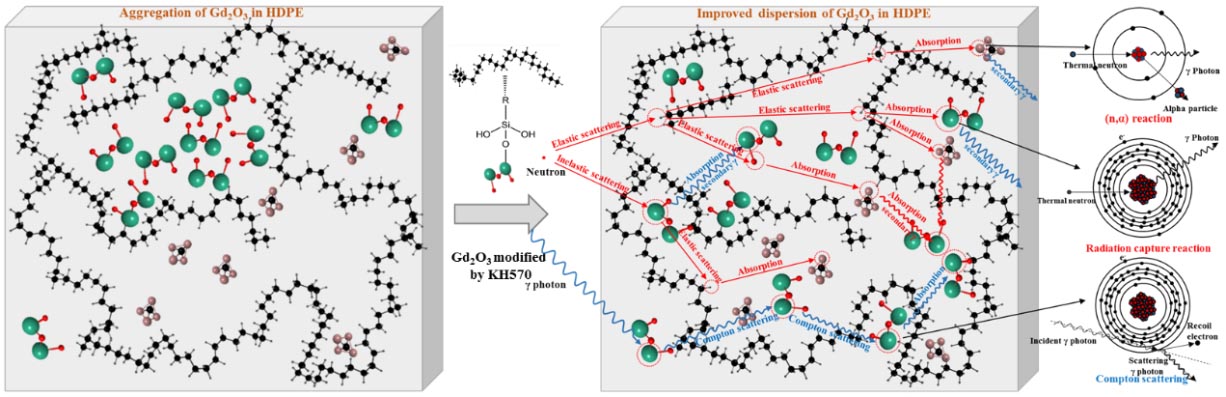
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of shielding mechanism of modified nano composite shielding material (Image by HUO Zhiping)
ZHAO Weiwei
Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (http://english.hf.cas.cn/)
Email: annyzhao@ipp.ac.cn