
Recently, a research team led by Prof. LIU Qingsong from Institute of Health and Medical Technology, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of Chinese Academy of Sciences, developed a novel Mammalian STE20-like protein 1 kinase (MST1) inhibitor for the treatment of type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D).
The results were published in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.
Currently, nearly 350 million people worldwide suffer from diabetes. Although with different etiologies, both T1D and T2D will cause the damage of β cells and disordered insulin-secretion function of β cells. Therefore, it is important to develop new approaches to achieve the goal of increasing the mass as well as improving the function of β cells.
MST1 is reported to play vital roles in the apoptosis and insulin secretion of β cells, and therefore it is a novel therapeutic target for β cell protection.
In this research, through a structure-guided drug design approach, scientists discovered a potent and highly selective inhibitor of MST1 (IHMT-MST1-58) which displayed many advantages.
The compound could inhibit the phosphorylation of MST1 and protect β cells from the damage of inflammatory cytokines in vitro. And it also exhibited good in vivo pharmacokinetic properties among different species including rats, mice, and beagle dogs.
Both monotherapy of IHMT-MST1-58 and in combination with metformin could decrease the fasting blood glucose (FBG) level and protect β cells in the STZ-induced type 1/2 diabetes mouse models. Furthermore, coadministration of IHMT-MST1-58 with metformin also reduced the hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level.
The study provided a new potential therapeutic candidate for diabetes.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
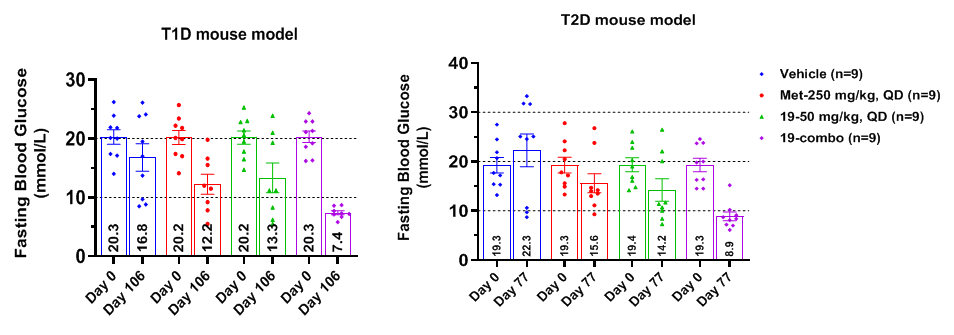
Antidiabetic efficacy of IHMT-MST1-58 (19), metformin, and combo in the T1D and T2D mouse models. (Image by WANG Beilei)