
According to a research published in International Journal of Radiation Oncology * Biology * Physics (Red Journal) recently, a team led by Prof. HAN Wei from Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) found, for the first time, that GOLPH3, a protein located in the extranuclear organelle Golgi apparatus, mediated the formation of radioresistance in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), and confirmed that GOLPH3 is a promising target for improving the efficacy of radiotherapy.
Radioresistance of tumor is one of the main reasons that affect the efficacy of radiotherapy, and it is also the most concerned problem in clinical radiotherapy research. Up to now, the mechanism of tumor radioresistance is still unclear.
GOLPH3, a novel oncoprotein, is closely related to the poor prognosis of various malignant tumors. The research team found that the level of GOLPH3 protein in tumor tissue of LUAD patients was significantly higher than that in adjacent tissues. Moreover, they found GOLPH3 positively regulated the level of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in various LUAD cells by inhibiting its degradation in lysosome, and promoted the accumulation of EGFR in the nucleus after irradiation. The nuclear EGFR triggered DNA-PK activation by forming a complex with DNA-PK, which enhanced the DNA damage repair and the resistance of LUAD to radiation.
Furthermore, through lentivirus infection and intratumoral injection of adenovirus, interference with the expression of GOLPH3 in LUAD cell lines and xenografts can significantly weaken the repair of DNA damage, promote cell death and inhibit tumor growth after irradiation, which confirms that targeted inhibition of GOLPH3 to reduce the radioresistance of LUAD has certain clinical value.
This research has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Natural Science Fund of Anhui Province and the HFIPS Director's Fund.
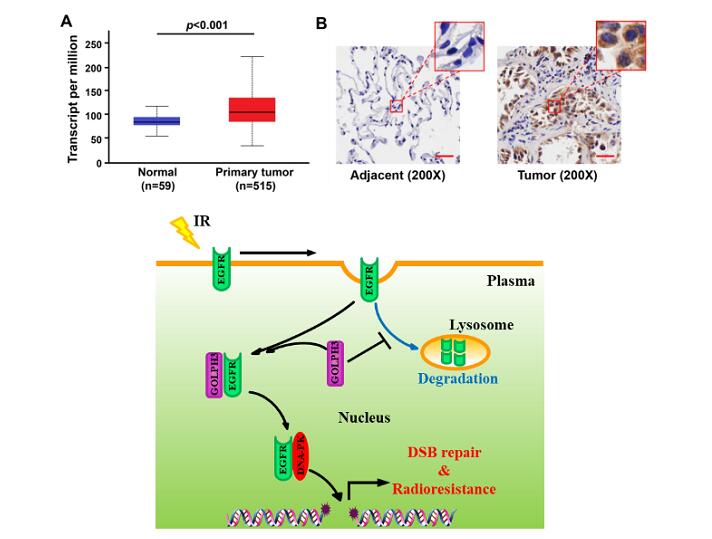
GOLPH3 mediates radioresistance formation of lung adenocarcinoma (Image by KONG Peizhong)

Inhibiting GOLPH3 can effectively reduce the radioresistance of lung adenocarcinoma (Image by KONG Peizhong)