
According to a research published in Advanced Materials, a collaborated team, which was led by Prof. YAN Wensheng from University of Science and Technology of China and Prof. SHENG Zhigao from High Magnetic Field Laboratory, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), systematically studied the coherent exciton-magneton coupling effect in two-dimensional Néel-type antiferromagnetic VPS3 by employing the superconducting magnet SM1 and ultrafast optics of SHMFF (Steady High Magnetic Field Fascility).
Two-dimensional (2D) van der Waals (vdW) antiferromagnetic materials have attracted extensive attention. In recent years, important progress has been made in the research of spin-orbit entangled exciton states and electron spin torque. However, due to the lack of net magnetization and external magnetic field response ability, it is still a serious challenge to accurately identify their magnetic structure and further understand their antiferromagnetic derivative effect, which greatly limits the basic research and practical application of two-dimensional antiferromagnetism.
In this research, in order to explore the magnetic configuration and its derivative effects of 2D antiferromagnetic materials, the research team used the nonlinear second harmonic (SHG) and Raman spectroscopy of SHMFF to study the layered antiferromagnetic single crystal VPS3.
The Néel-type antiferromagnetic order in the two-dimensional antiferromagnetic VPS3 with out-of-plane anisotropy was revealed. They also found that this long-range antiferromagnetic order still existed in the ultra-thin limit.
Subsequently, the strong interlayer exciton-magneton coupling (EMC) induced by Néel-type antiferromagnetic order and its enhanced exciton state were detected in the monolayer WSe2 / VPS3 heterojunction for the first time.
"The strong exciton-magneton coupling behavior caused by this configuration and the fine magnetic structure of VPS3 have never before been demonstrated experimentally," said HOU De, member of the team.
This research provided a new optical approach for the study of 2D antiferromagnetic materials and promoted their potential applications in magnetic-optical and optical-spin electronic devices.
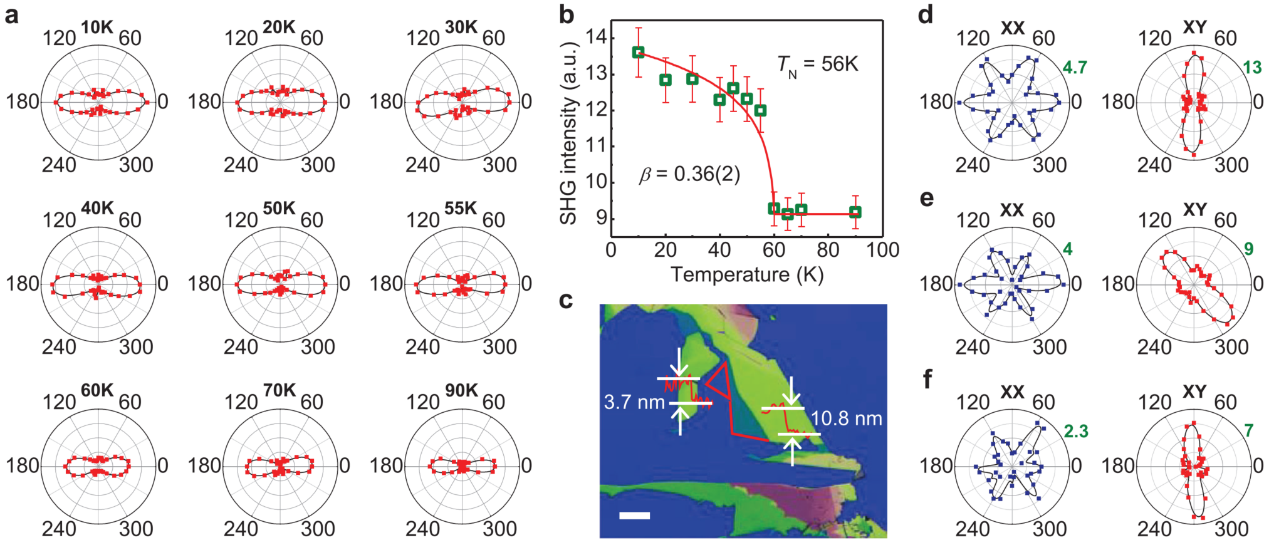
Fig.1 SHG patterns of VPS3 samples. (Image by HOU De)