
Recently, a collaborated research team led by Prof. WANG Huanqin from the Institute of Intelligent Machines, the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, has developed a semi-supervised convolutional neural network (CNN) to assist in the cytological diagnosis of pancreatic cancer from endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) smear specimens.
The related research results were published in BMC Cancer.
EUS-FNA is currently the most reliable and minimally invasive diagnostic method for pancreatic cancer. The rapid on-site evaluation (ROSE) involving pathologists can significantly improve the quality of smear specimens, reduce the number of punctures, and lower the risk of complications. Therefore, the demand for ROSE from endoscopists is increasing. However, the shortage of pathologist human resources and their heavy workload are common problems.
In this study, the team proposed a semi-supervised CNN-based segmentation model specifically for cytological specimens of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). This model can automatically distinguish between cancerous and non-cancerous cell clusters in EUS-FNA smears.
Performance evaluations showed that the AI model achieved diagnostic accuracy comparable to that of senior pathologists and surpassed that of junior and intermediate-level practitioners. Specifically, the positive predictive value reached 96% for the AI model, compared to 93% for senior pathologists, 84% for intermediate, and 73% for junior pathologists.
This approach not only reduces the reliance on ROSE, but also minimizes the annotation burden for expert pathologists by leveraging semi-supervised learning—making it a promising tool for improving the efficiency and consistency of pancreatic cancer diagnosis.
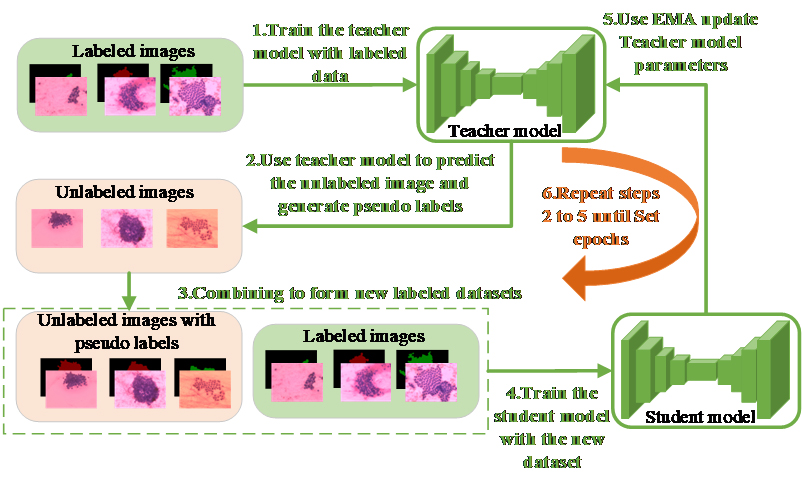
Semi-supervised learning method for segmentation of cancer cell clusters in pathological smears. (Image by WANG Huanqin)