
A research team from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with the Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University, has developed a highly accurate blood-based biomarker panel for distinguishing invasive from non-invasive pituitary adenomas.
Their findings were recently published in BMC Medicine.
Pituitary adenomas (PAs) are common benign brain tumors, but around 30–40% of cases display invasive behavior, which leads to increased recurrence rates and greater treatment challenges. Accurately identifying invasive pituitary adenomas (IPA) before surgery remains difficult with current imaging and pathology techniques. In response to this clinical need, the research team focused on cell-free DNA (cfDNA) methylation profiling as a novel, non-invasive approach to tumor detection.
By integrating reduced representation bisulfite sequencing and RNA sequencing data from tumor tissues and matched plasma samples, the researchers built a comprehensive multi-omics landscape of IPA and non-invasive PAs (NPA). Their analysis included 129 samples from patients with IPAs and NPAs, along with healthy controls.
Through this approach, they identified 17 genes with both abnormal methylation and altered expression, ultimately narrowing down to a trio of key biomarkers: MIR4535, SLC8A1-AS1, and TTC34. A diagnostic panel based on methylation signatures of these genes demonstrated exceptional accuracy in plasma samples, with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.980 for distinguishing IPA from NPA and 0.990 for distinguishing NPA from healthy individuals.
"Our results offer a new strategy for the early, non-invasive diagnosis of invasive pituitary adenomas," said ZHAO Ningning, a member of the team, "This biomarker panel could improve clinical decision-making and patient outcomes."
The study also provides a foundation for deeper investigation into the molecular mechanisms of tumor invasiveness. Future research involving larger cohorts and refined sample stratification, supported by advanced bioinformatics, may further improve diagnostic tools and therapeutic strategies for pituitary adenomas.
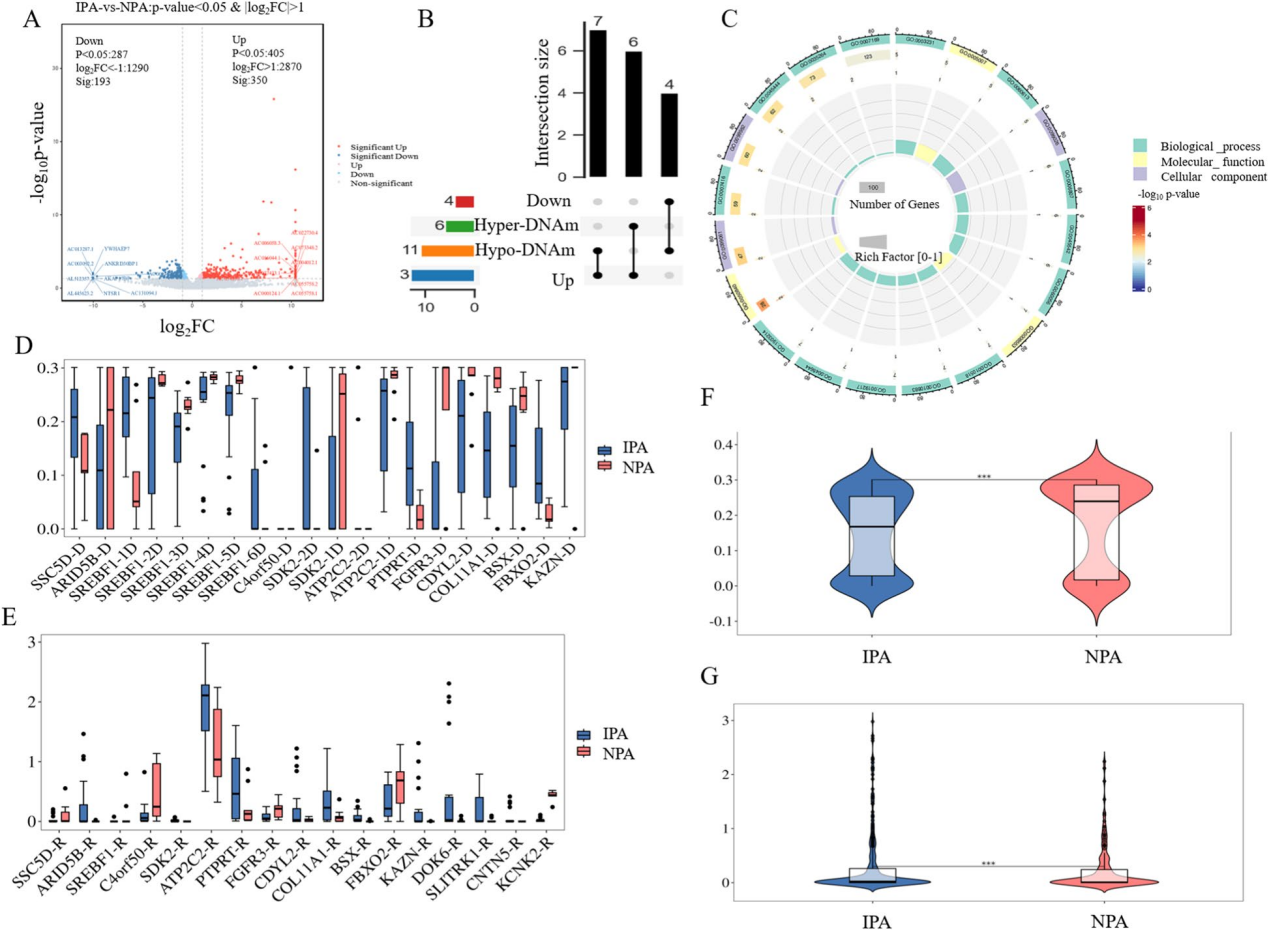
Correlation analysis between differentially methylated regions and gene expression. (Image by ZHAO Ningning)
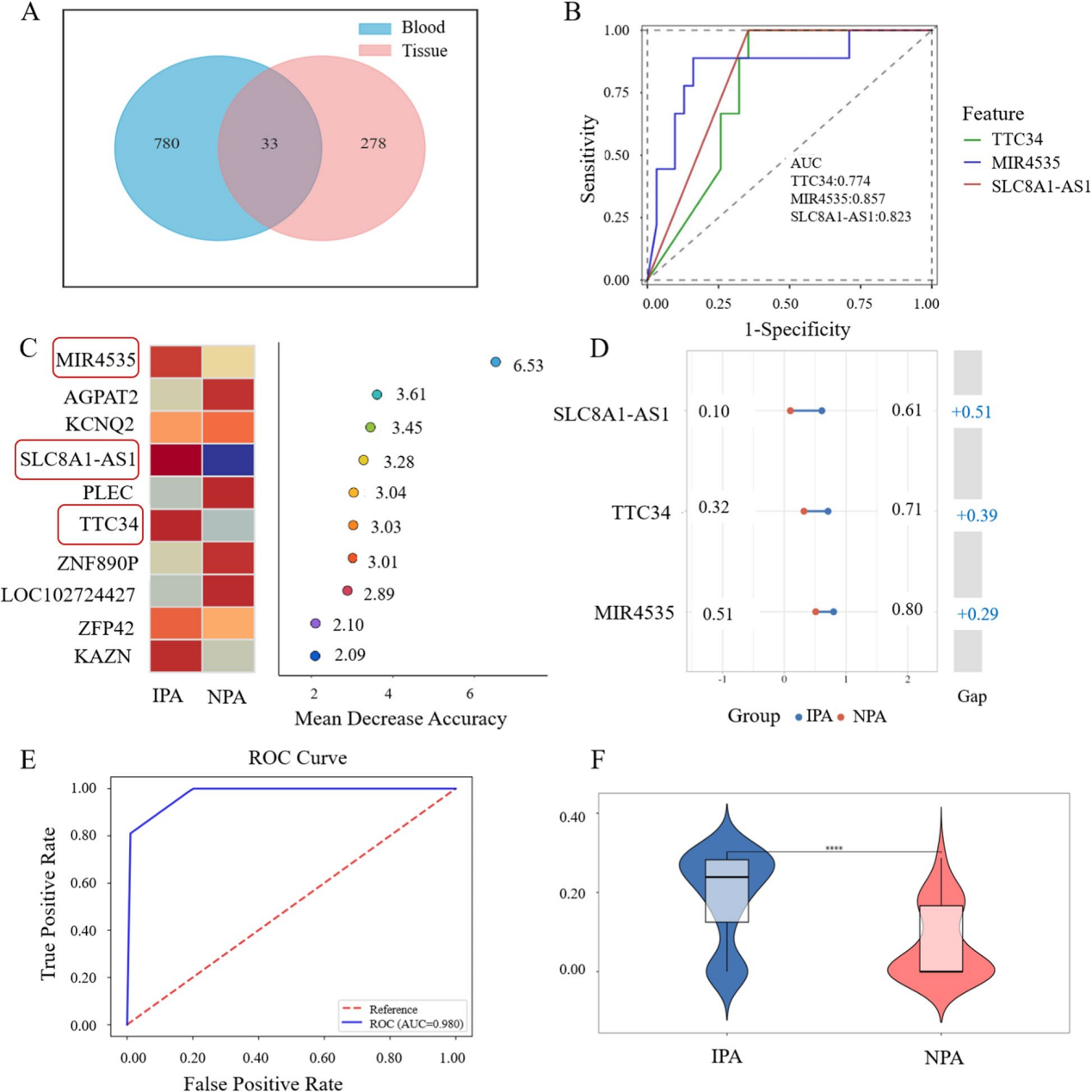
Identification of cfDNA biomarkers for screening IPA from NPA. (Image by ZHAO Ningning)