
In a recent study published in Analytical Chemistry, a research team led by WANG Junfeng from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a novel immobilization method for surface plasmon resonance (SPR) assays of membrane proteins, effectively addressing major technical constraints in the field.
Membrane proteins make up about one-third of human proteins and nearly 60% of drug targets, playing key roles in signaling and transport. Accurately measuring their interactions with ligands is vital for understanding function and drug development. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR), a gold-standard, label-free technique allows real-time analysis of binding kinetics. However, applying SPR to membrane proteins is difficult due to challenges in stably immobilizing them while maintaining their native structure and activity.
To address this challenge, the research team integrated the SpyCatcher-SpyTag covalent conjugation system with membrane scaffold protein (MSP)-based nanodisc technology to develop a simple, efficient, and stable strategy for immobilizing membrane proteins on sensor chips. The approach involves generating an MSP-SpyTag fusion protein to incorporate the target membrane protein into lipid nanodiscs. The resulting nanodiscs carry the SpyTag label, allowing highly specific and efficient capture by SpyCatcher proteins pre-immobilized on a CM5 chip via standard amine coupling. This method facilitates robust and stable immobilization of membrane proteins within a near-native lipid environment.
Employing this approach, the team performed SPR analysis on three representative types of membrane protein interactions: protein–lipid, transmembrane protein–antibody, and transmembrane protein–small molecule. The method consistently generated high-quality SPR data, enabling precise quantification of binding kinetics and affinities.
This novel approach effectively addresses the key bottlenecks of SPR technology in membrane protein studies, holding significant potential for advancing membrane protein research and drug discovery
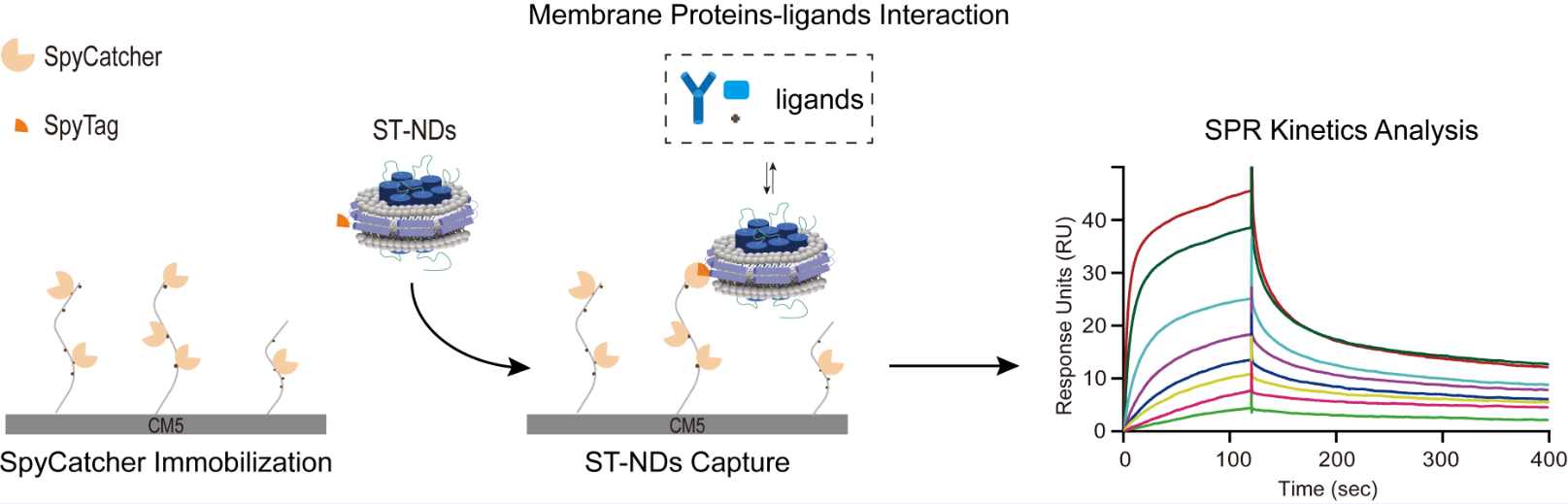
Schematic of the SpyCatcher-SpyTag-mediated covalent immobilization strategy for membrane protein SPR analysis (Image by WU Bo)