
A research team led by CHEN Lei from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, together with collaborators from Shanghai AI Laboratory and The Chinese University of Hong Kong, has developed GoRA, a gradient-driven adaptive low-rank fine-tuning framework for large language models.
Their paper has been accepted by NeurIPS 2025.
As large language models continue to expand, low-rank adaptation (LoRA) has become an essential tool for efficient fine-tuning, helping reduce computational and memory costs. Yet existing LoRA methods still struggle with two core issues—how to choose the appropriate rank and how to initialize low-rank weights—often resulting in unstable training and limited performance.
GoRA provides a unified solution to these challenges. By leveraging gradient information from pre-trained weights, it automatically assigns an optimal rank to each adapter before training and adaptively initializes low-rank matrices through gradient compression. This approach preserves all original model weights, eliminating the “weight inconsistency” problem between training and inference, while improving fine-tuning performance with minimal additional overhead.
Fully compatible with standard LoRA, GoRA integrates smoothly into existing large-model pipelines and supports distributed training. Its adaptive gradient accumulation and automatic scaling-factor adjustment further reduce the burden of hyperparameter tuning, making the framework highly plug-and-play.
Benchmark evaluations show clear and consistent gains. On the GSM8K mathematical reasoning benchmark, GoRA boosts the Llama3.1-8B-Base model’s accuracy by 5.13 points over standard LoRA and, at higher ranks, even outperforms full fine-tuning. Across tasks including GLUE, HumanEval, MT-Bench and CLIP-ViT, GoRA surpasses other LoRA variants, demonstrating strong cross-architecture and cross-modal adaptability.
These findings highlight GoRA as a promising new direction for efficient large-model fine-tuning and offer new opportunities for lightweight model deployment in resource-constrained environments.
The research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
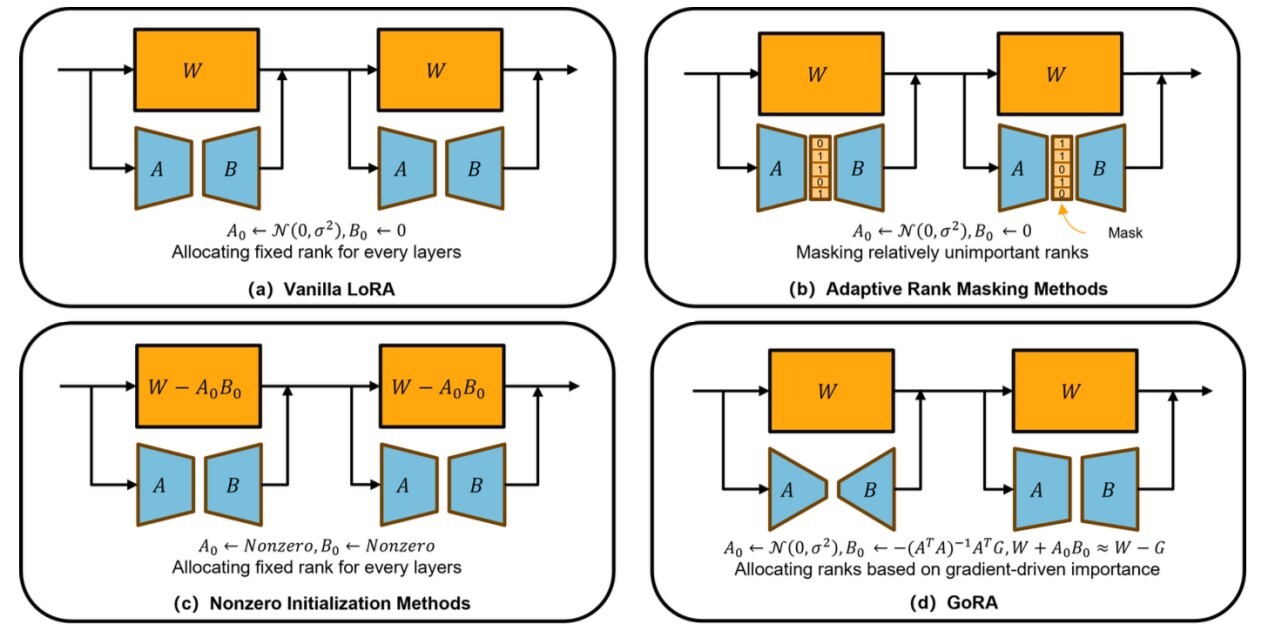
The difference between GoRA method and other methods (Image by CHEN Lei)