
Recently, a research team led by Prof. WANG Hongzhi and Prof. HONG Bo from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Prof. WANG Wei from the First Affiliated Hospital of the University of Science and Technology of China, uncovered a key mechanism underlying chemotherapy resistance and metastasis in small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Their study shows that epigenetic silencing of the RASA4 gene plays a crucial role in driving disease progression.
The findings were published in Communications Biology.
Small cell lung cancer is an aggressive cancer with a poor prognosis. Although many patients initially respond to chemotherapy, drug resistance often develops rapidly, leading to tumor progression and metastasis. The molecular mechanisms behind this process, particularly those involving epigenetic regulation, have remained poorly understood.
In this study, the researchers analyzed DNA modification patterns in tumor tissues and blood samples from SCLC patients. They found that the RASA4 gene was consistently “switched off” in patients with progressive disease. Importantly, restoring RASA4 activity in cancer cells reduced tumor growth, invasiveness, and resistance to chemotherapy.
Further experiments revealed that loss of RASA4 removed a key brake on cancer-promoting signaling pathways, enabling cancer cells to become more aggressive and acquire features associated with metastasis and drug resistance. Clinical analysis of patient samples confirmed that RASA4 levels were markedly lower in SCLC tumors and that reduced expression was closely associated with poorer patient outcomes.
This study identifies RASA4 silencing as a central driver of malignant progression in small cell lung cancer, highlighting its potential value as both a biomarker for disease progression and a promising target for future therapies.
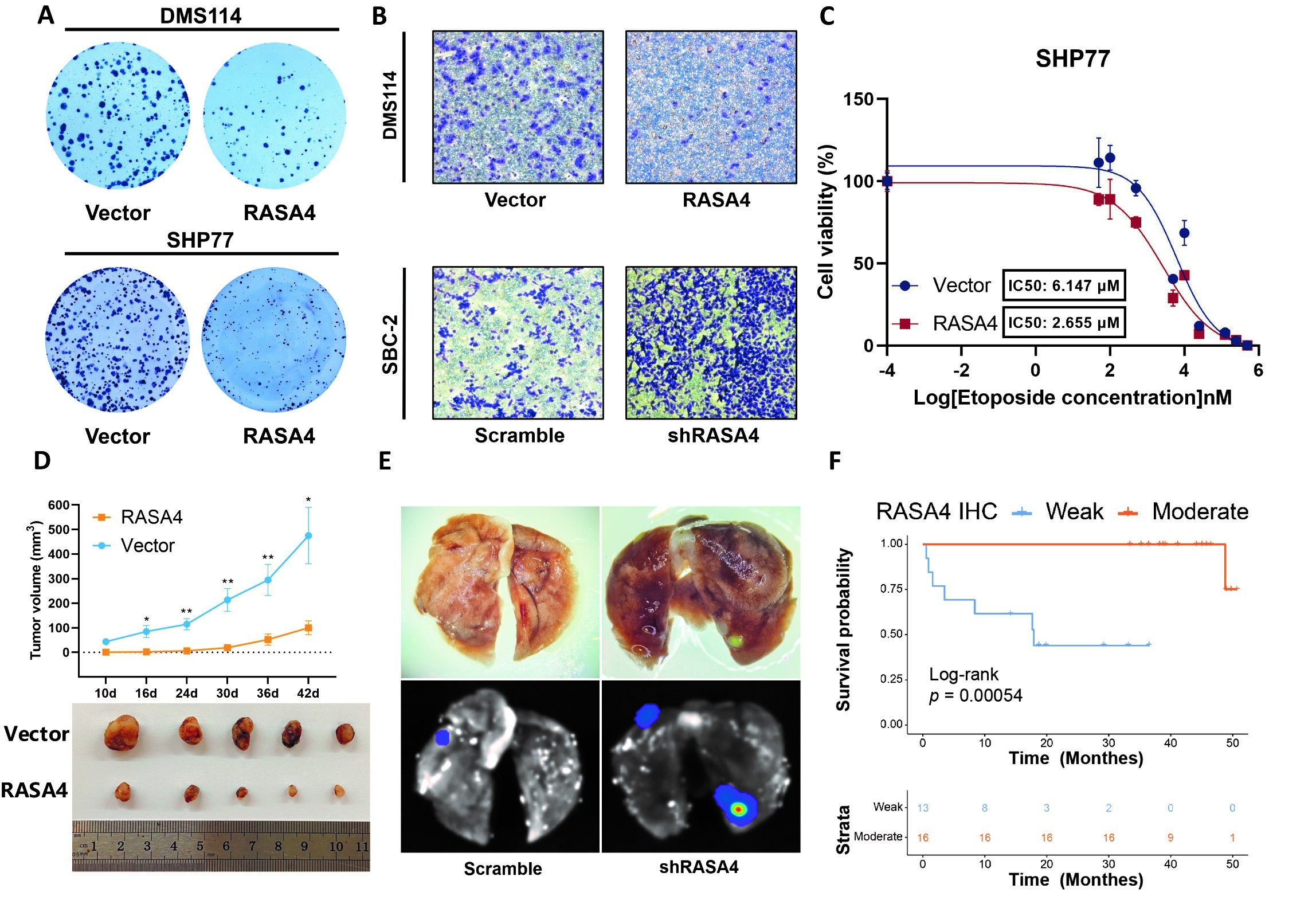
Epigenetic silencing of RASA4 promotes proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance in SCLC, thereby leading to poor clinical prognosis. (Image by FU Meng)