
Recently, a research group led by Prof. ZHANG Haimin from the Institute of Solid State Physics, Hefei Institute of Physical Science (HFIPS) reported a highly efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction by in situ generation and systematically illustrated the origin of its excellent performance, which provided a new method for exploiting excellent OER catalysts.
"This is an efficient and low-cost transition metal phosphide (TMP) electrocatalyst by a novel impregnation-pyrolysis synthetic method.” explained WANG Haojie, a doctoral student who joined the team.
Through chemical activation and pyrolysis, in this research, the natural cotton became an excellent porous support for synthesizing and stabilizing the ultrafine Ni12P5 nanoparticles. The well-designed TMP catalyst showed remarkable OER performance, and its structure evolution during OER was systematically investigated.
They investigated a series of (FexNiy)12P5@PPC electrocatalyst, and found (Fe0 .25Ni0.75)12P5@PPC exhibited an outstanding OER performance, smaller overpotentials and fast kinetics process, which is superior to commercial RuO2 and other reported excellent catalysts. An abnormal change of the chronopotential curves during OER test make them believe that the structure of (Fe0.25Ni0.75)12P5@PPC had changed. Besides, the Fe-doped Ni12P5 nanoparticles reconstructed NiFe2O4 with low-crystallinity and high-spin Fe4+, which was proven to be the catalytic active species for highly active OER.
Their findings systematically characterized the structural reconstruction of excellent TMP electrocatalyst during OER, clarified the origin of its high OER activity.
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51872292) and Collaborative Innovation Program of Hefei Science Center, CAS (No. 2019HSC-CIP009).
Link to the paper: In-situ transformation of Fe-doped Ni12P5into low-crystallized NiFe2O4 with high-spin Fe4+ for efficiently electrocatalytic water oxidation
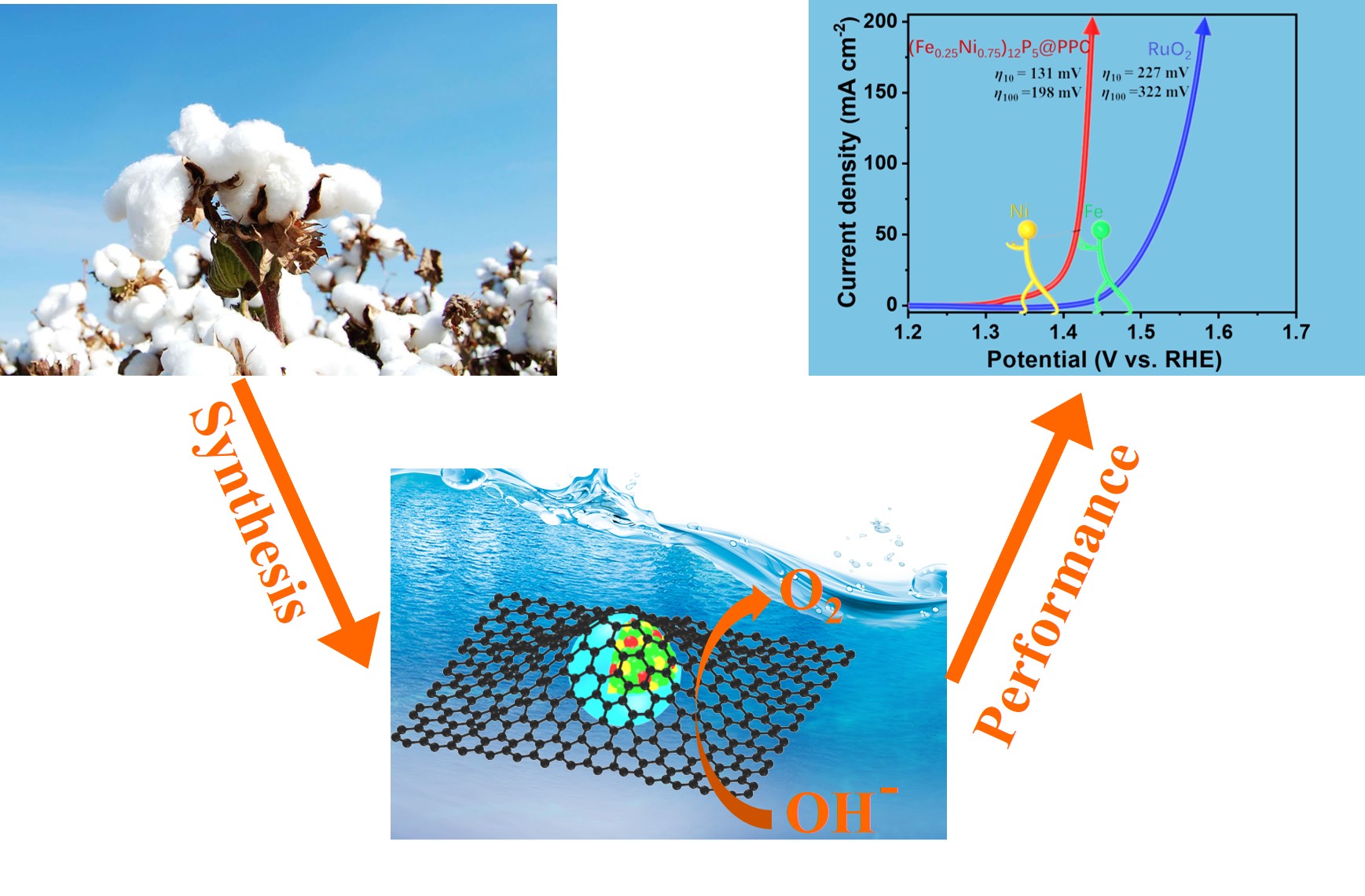
The graphical abstract (Image by WANG Haojie)
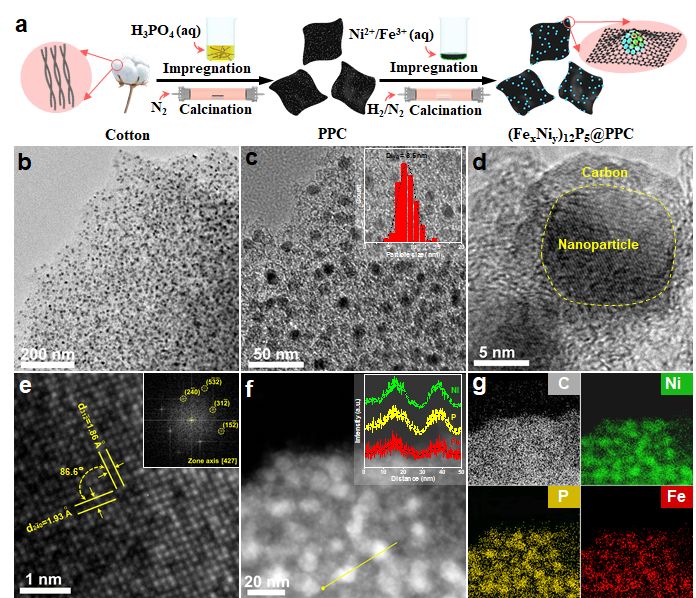
Fig. 1. (a) The synthetic process; (b-e) TEM and HRTEM images, (f) HAADF-STEM image, and (g) EDS mapping images of (Fe0.25Ni0.75)12P5@PPC (Image by WANG Haojie)
Contact:
ZHAO Weiwei
Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (http://english.hf.cas.cn/)
Email: annyzhao@ipp.ac.cn