
A research team led by Prof. Xu‘an and Assoc Prof. LIU Yun from Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), successfully demonstrated the effective, specific and safe detoxification effect and its related mechanism of zinc oxide/graphene oxide (ZnO/GO) nanocomposites against Cd-induced hepatotoxicity, with the help of 9.4T high field magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the High Magnetic Field Laboratory of HFIPS
The results were recently published in Environment International.
Epidemiologic and laboratory studies have associated environmental Cd exposure with various liver damages, including hepatic necroinflammation, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and even liver cancer. However, there is no effective and specific detoxification method for Cd poisoning in current clinical treatment. The symptomatic treatments and non-specific metal ion chelating agent currently used in clinic have limited therapeutic effects and will inevitably cause adverse side-effects.
To solve this problem, the team further synthesized ZnO/GO nanocomposites with good biocompatibility, and indicated their advanced function against Cd-elicited liver damage at the in situ level in vivo by 9.4T high field MRI. They concluded that, mechanistically, ZnO/GO nanocomposites competitively inhibited the cellular Cd uptake through releasing Zn ions, and significantly promoted Cd excretion via targeting the efflux pump of multidrug resistance associated protein1 (MRP1).
The synthesized ZnO/GO nanocomposites with excellent detoxification capacity and favorable biosafety will hold great promise for potential applications in Cd poisoning, especially for occupational exposure population who exposed to Cd in their daily work.
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China grants (22076191), Youth Innovation Promotion Association of CAS (Grant No.2020444), Anhui Provincial Key R&D Programs (202004i07020015) and so on. A portion of this work was performed on the Steady High Magnetic Field Facilities, High Magnetic Field Laboratory, CAS; and supported by the High Magnetic Field Laboratory of Anhui Province.
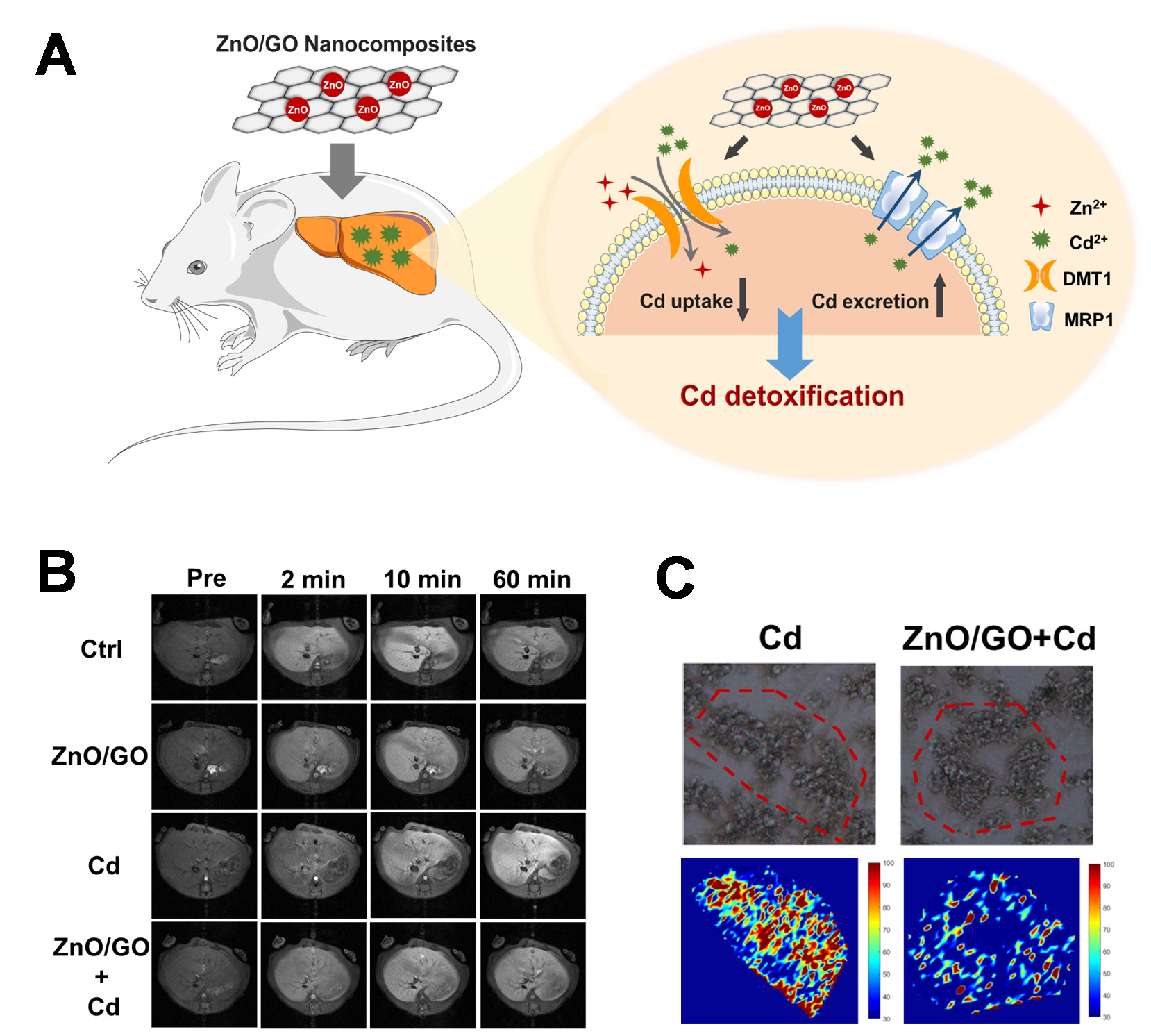
(A) Schematic diagram illustrating the mechanisms involved in the antagonistic process of ZnO/GO nanocomposites against Cd-induced hepatotoxicity. (B) High field MRI verified the protective role of ZnO/GO nanocomposites against Cd-induced hepatic injuries. (C) LA-ICP-MS indicated that ZnO/GO nanocomposites reduce the bioaccumulation of Cd. (Image by LIU Yun)