
A research team led by Dr. WU Yuejin from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, discovered that the SM1 gene plays a crucial role in the development of rice leaf veins and affects methane emissions from rice plants.
Their findings were published in Plant Science.
Rice leaf veins are essential for the plant's growth and development. They help support the leaves and transport important substances like water, gases, and nutrients throughout the plant. However, scientists didn't fully understand molecular underlying mechanism how these veins form and develop.
In this study, the team used ion beam mutagenesis technology and identified a rice mutant, which leaf veins become solid instead of hollow. These mutant plants were shorter and had 49% less dry weight compared to their wild type plants. Through further research, the team identified a key gene, named SM1, that plays a crucial role in controlling the development of rice leaf veins.
The SM1 gene encodes a litter zipper protein that interacts with another protein, OSHB1, to regulate the expression of OSH1, which controls the growth of the plant's stem cells. This interaction affects how the rice plant's vascular system develops.
Researchers also discovered that in the mutant plants, the solid veins were filled with different types of cells, which limited the plant's ability to transport oxygen to its roots. This led to enhanced methanogenic activity in the rhizosphere and a 96.8% increase in total methane emissions.
This research highlights the importance of the rice plant's vascular system in both growth and methane emissions. It also provides new ideas for rice breeding.
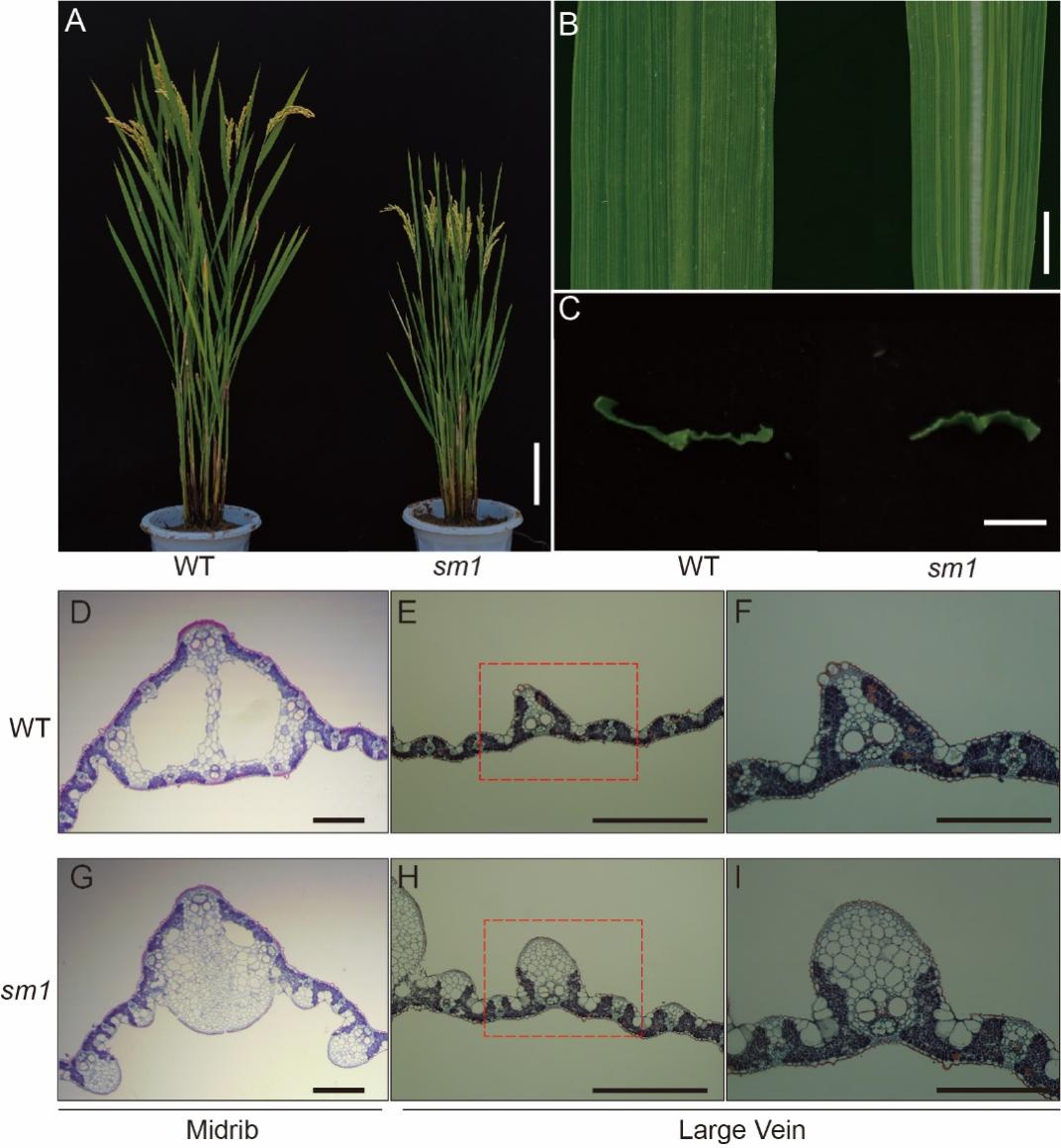
Phenotypic Analysis of SM1 Mutant (Image by YE Yafeng)
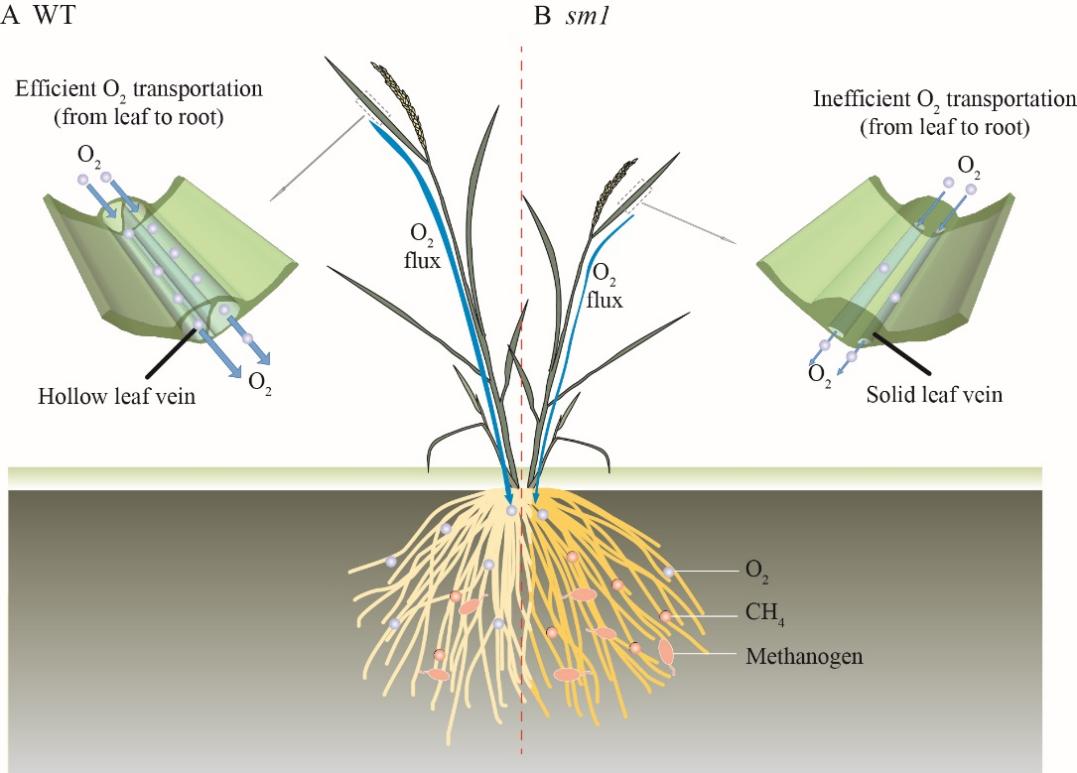
Working Model of the SM1 Gene (Image by YE Yafeng)