
A research team led by Prof. ZHANG Zhirong from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, developed a novel sensor that enabled simultaneous, highly sensitive detection of multiple stable heavy isotopes in exhaled carbon dioxide.
The findings were recently published in Analytical Chemistry.
Breath analysis has become an increasingly attractive tool in medical diagnosis due to its non-invasive, safe, and fast nature. Among the various markers in exhaled breath, CO2 and its stable isotopes play a key role—particularly in tests like the ^13C-urea breath test, which is widely used to detect Helicobacter pylori infections. However, traditional hollow waveguides restricts the interaction between light and gas molecules and reduces measurement sensitivity.
In this study, the team introduced a novel mid-infrared enhanced hollow waveguide (EHWG) sensor.
"The inspiration is from advanced optical techniques," explained Prof. ZHANG, "and we incorporated high-reflectivity mirrors into the waveguide structure."
The new sensor is capable of simultaneously analyzing multiple isotopes in exhaled CO₂ with greater precision than previously achieved. Its performance was further validated through real breath samples, showing strong consistency with results from standard hospital tests. The results highlight the sensor' s potential as a practical tool for clinical applications.
In addition to improved sensitivity and reliability, the EHWG sensor also offers advantages such as compact size, lightweight design, and suitability for use with small sample volumes. These features make it a promising candidate for next-generation breath diagnostic devices in medical settings.
"This study demonstrates that EHWG has great potential in manufacturing miniaturized, broad-spectrum, and lightweight gas sensors," added Prof. ZHANG, "and is expected to become the first choice for small-volume sample gas measurement."
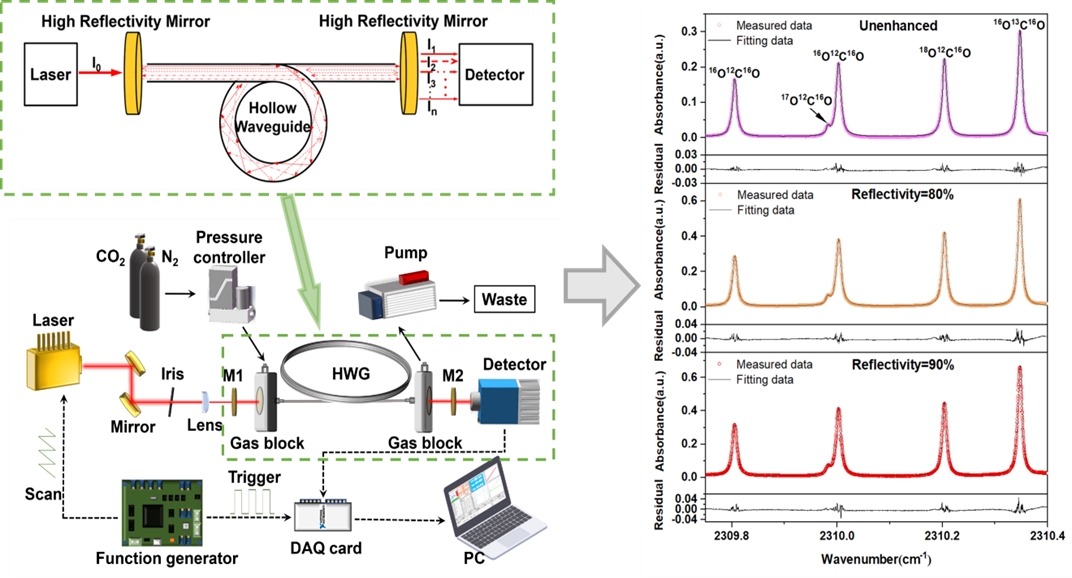
Schematic illustration of the enhanced hollow waveguide gas isotope sensor. (Image by HUANG Wenbiao)