
Recently, a research group led by Prof. SUN Xiaobing from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, investigated the impact of multiangular polarimetry on the quantification of marine aerosol remote sensing applications.
Their findings were published in the Optics Express.
Aerosols are one of the most uncertain components in the quantification of climate radiative forcing, while polarimetry helps to improve the characterization of the microphysical properties of atmospheric aerosol.
In this study, the team investigated the importance of the spectral range, the spectral band, the number of viewing angles, and the polarimetric accuracy for aerosol retrieval from polarization measurements over the ocean. Based on Bayesian optimization theory and a vector radiative transfer model, the research team employed the degrees of freedom for signal (DFS) as an indicator to compare and analyze different observation scenarios.
Experimental results showed that DFS can be increased by at least 1.02 with the addition of shortwave infrared (SWIR) intensity and polarization measurements in the single-angle observation mode. This improvement corresponds to the retrieval of one to two additional aerosol parameters. In the multi-viewing experiment, the columnar volume concentration, effective radius, and complex refractive index for both fine and coarse size modes benefit from additional viewing angles.
Furthermore, incorporating additional multi-angle SWIR measurements can enhance the total aerosol DFS by approximately 1.1-3.3. The analysis also indicated that the polarimetric accuracy has a significant impact on the uncertainty of aerosol retrieval.
This research provided an important reference for the design of future polarimetric instruments and the development of retrieval algorithms.
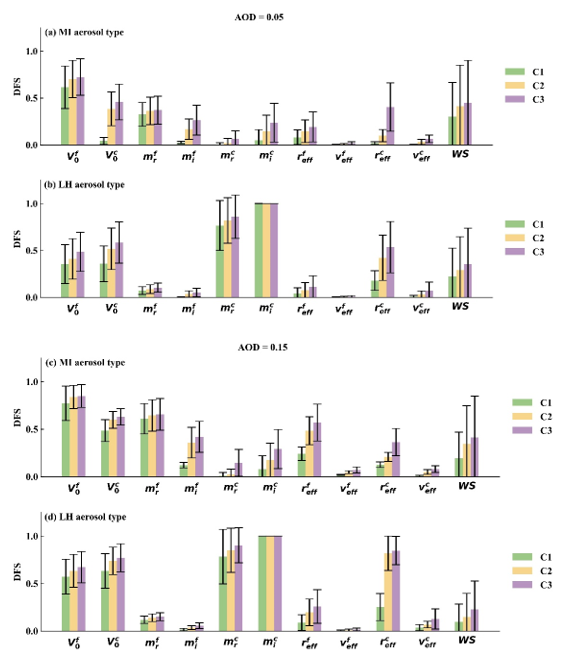
The individual DFS for each aerosol parameter and one sea surface parameter for the two aerosol models in the single-angle observation mode. (Image by SUN Xiaobing)
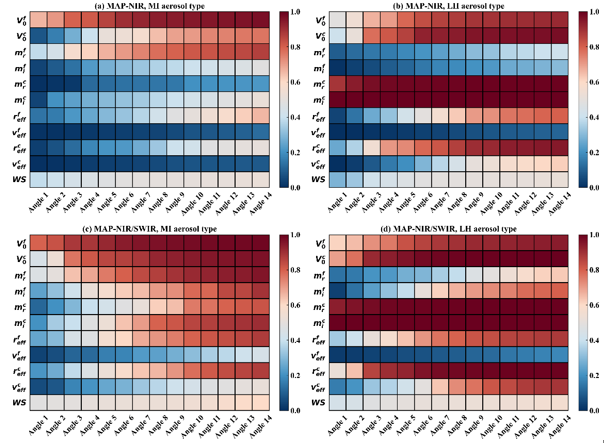
The variation of DFS of aerosol and wind speed parameters with observation angles in the multi-angle observation mode. (Image by SUN Xiaobing)