A Chinese joint team realized the first discovery of a flat band in realistic Quasi-2D kagome-patterned Fe3Sn2 crystal and they also proposed its mechanism of high temperature ferromagnetism.
The work was done by a joint team of LU Qingyou with High Magnetic Field Laboratory, or SHMFF and ZENG Changgang with University of Science and Technology of China, or USTC. And their joint work was published on Physical Review Letters as the cover paper.
In the band theory of electrons, the band structures of a solid are obtained by solving single-electron Schrodinger equation for the electrons in a periodic potential system. And, various important band structures can be created by adopting properly designed lattice structures.
A flat band is a highly degenerate and dispersionless manifold state of electrons and may tender exceptional opportunities for the development of exotic quantum phases.
Although many lattice structures have been proposed to generate flat bands, to date evident flat bands have not been realized in real materials.
Actually, in an Fe3Sn2 crystal, the two Fe-Sn layers are seperated by a Sn layer, in which the Fe atoms in an Fe-Sn layer form a Kagome lattice (a traditional woven bamboo pattern).
And theoretical calculations showed that the Kagome lattice can cause the local destructive interferences of Bloch wave functions, thus resulting in the band flatness.
In the study, the team measured the magnetism of Fe3Sn2.
The lab results showed that each Fe atom has a saturation magnetic moment of approximated 1.94 μB when the temperature is at 2 K and the Curie temperature Tc is around 610 K.
And the hexagonal unit network in the Kagome lattice promoted the ferromagnetic coupling of the local spin moments formed by intramolecular exchange interaction.
Using their home-built high sensitivity magnetic force microscope (or MFM), the team have achieved success in direct observation of the magnetic structure in Fe3Sn2.
The clearly observed magnetic domains in stripes confirmed that the long-range ferromagnetic orderings do exist in Fe3Sn2.
The study revealed, for the first time, the existence of flat bands in the realistic quasi-2D Kagome-patterned Fe3Sn2.
In addition to the first time confirmation, it further showed that the flat bands possess local spin polarization originated from an intramolecular exchange interaction together with the long-range ferromagnetic order through hexagonal cell network.
Regulating the flat-band electronic structures (via charge doping for instance) may realize other significant quantum phenomena.
The above work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, etc.
Link to the paper: Flat bands and emergent ferromagnetic ordering in Fe3Sn2kagome lattices
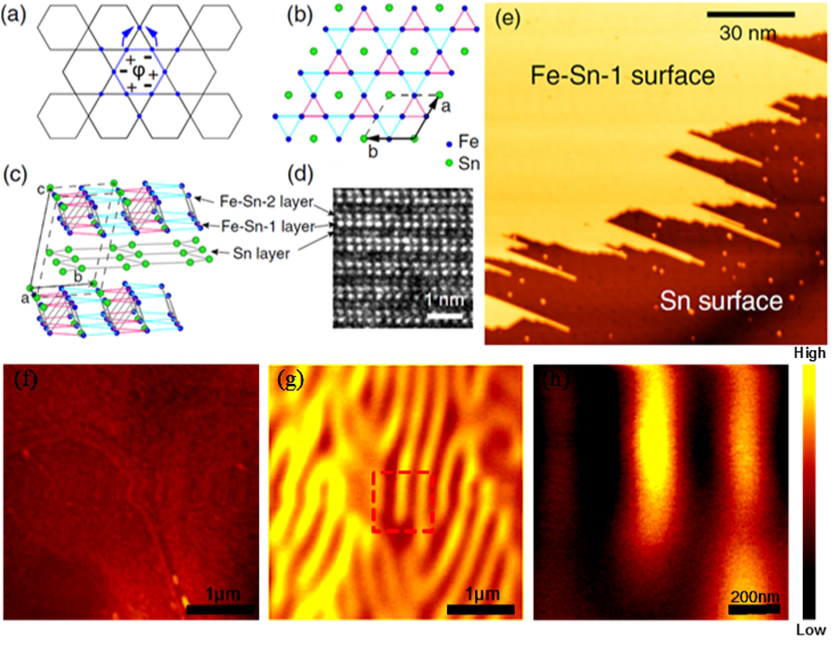
Structural characterization and ferromagnetism of the Fe3Sn2 bulk and surface : (a) Schematic diagram of the wave function self-localization on the hexagons in the Kagome lattice (b);(c) Schematic diagram of top and side view of Fe3Sn2; (d)Cross-sectional TEM image with atomic resolution for three different layers; (e) Large-range STM image of a cleaved Fe3Sn2 surface with two different surface layers;(f), (g) AFM and MFM images of the same area on Fe3Sn2; (h) Zoom-in scan MFM image of the rectangle area in (g). (Image by GUO Tengfei)
Contact:
ZHOU Shu
Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (http://english.hf.cas.cn/)
Email: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
 Tel: +86-551-65591206
Tel: +86-551-65591206
 Fax: +86-551-65591270
Fax: +86-551-65591270
 Emai: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
Emai: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
 350 Shushanhu Road
350 Shushanhu Road