Chinese scientists conducted research on 1.06 μm near-infrared laser crystals and they obtained improvement in high power laser operation.
This work was done by SUN Dunlu’s research group at Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (AIOFM), Hefei Institutes of Physical Science.
1.06 μm laser has been widely used in the fields of processing, medical treatment, communication and so on.
Yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) crystals doped with Nd3+ have many advantages, thus, the crystals are suitable for high power laser operation. However, the Nd3+ single-doped YAG crystal pumped by a flash lamp still has the problems of low laser output energy and efficiency.
To tackle the problems above, the team proposed to improve the pumping efficiency of the flash lamp by co-doping Cr3+ as the sensitizer.
At the same time, the co-doping Cr3+ could also improve the radiation resistance of Cr,Nd:YAG crystal.
The Cr,Nd:YAG crystal with high optical quality has been successfully grown byCzochralski (Cz) method. Compared with the Nd:YAG crystal doped with the same concentration of Nd3+, the Cr,Nd:YAG crystal had higher laser output average power and efficiency operated at 1.06 μm under the same conditions. Additionally, the laser beam quality of the Cr,Nd:YAG crystal was comparative with that of the Nd:YAG crystal.
The results indicate that the Cr,Nd:YAG could be a promising laser crystal with higher laser performance and stronger radiation-resistant ability, which is expected to be applied to high-power systems and radiant environments.
Link to the paper: Influence of Cr3+doping on the spectroscopies and laser performance of Cr,Nd:YAG crystal operated at 1.06 μm
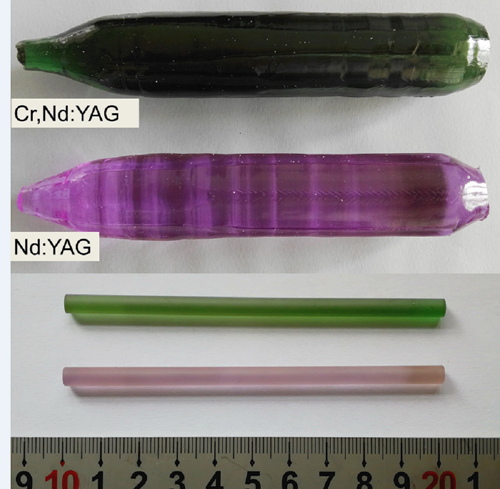

Photograph of Nd:YAG and Cr, Nd:YAG crystals and processed laser crystal rods. (Image by ZHANG Huili)
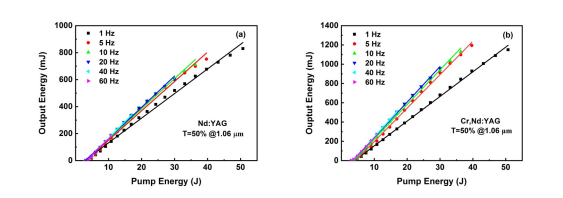
Output energy versus pump energy of the Nd:YAG and Cr, Nd:YAG crystals operated at different repetition rates with an output coupler transmission of 50%. (Image by ZHANG Huili)
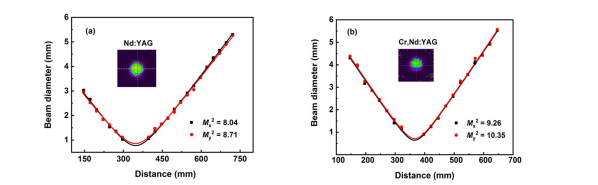
Beam diameter versus the distance of the Nd:YAG and Cr, Nd:YAG crystals. (Image by ZHANG Huili)
Contact:
ZHOU Shu
Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (http://english.hf.cas.cn/)
Email: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
 Tel: +86-551-65591206
Tel: +86-551-65591206
 Fax: +86-551-65591270
Fax: +86-551-65591270
 Emai: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
Emai: zhous@hfcas.ac.cn
 350 Shushanhu Road
350 Shushanhu Road