
A team led by Prof. WU Zhengyan from Institute of Intelligent Machines, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science recently introduced a high-efficiency Z-scheme photocatalyst to deal with contaminants in water.
This new solution has been published in ACS Applied Nano Materials.
In recent years, the rapid industrialisation has caused increasingly severe environmental pollution. Therein, kinds of organic pollutants in water have become major threats for human health and the ecosystem security worldwide. Therefore, an effective treatment approach has become an urgent task for elimination of organic pollutants at present.
In this research, the Bi2WO6(CdTeQDs/2DBWO) photocatalyst with a giant built-in electric field (BEF) was proved to extremely promote the dissociation of exciton and generation of reactive oxygen species. Scientists demonstrated BEF played a positive role during photocatalytic process, which exhibited much higher photodegradation efficiency for phenol, rhodamine B, and tetracycline compared to the pure Bi2WO6 under the visible light.
Compared to the commercial TiO2 photocatalyst, self-prepared CdTeQDs/2DBWO photocatalyst exhibited a slight advantage in photocatalytic efficiency for contaminants. However, due to a complicated synthesis process and a high cost, self-prepared photocatalyst is difficult to be applied in practical application, at present.
This study opened up a new route to design a high-efficiency photocatalysts.
This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China, the Science and Technology Service Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Science and Technology Major Project of Anhui Province and the Key R&D Program of Ningxia Province.

Figure 1. The prepared CdTeQDs/2DBWO photocatalyst with different proportions. (Image by YANG Pengqi)
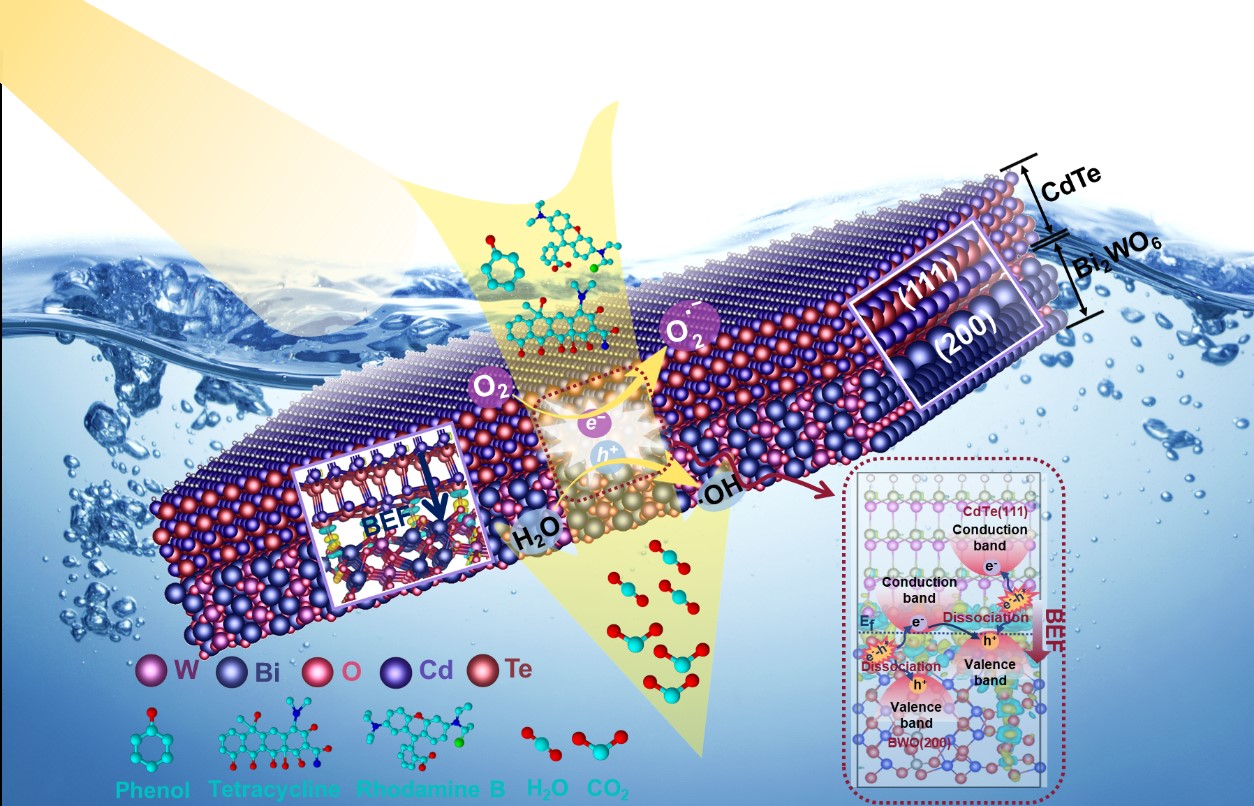
Figure 2. Schematic illustration of photocatalytic degradation mechanism. (Image by YANG Pengqi)